Terms in this set (7)
Q. Why is it important for light dependent reactions to separate water?
Explanation: Water is absolute requirement for photosynthesis to occur. During Light reactions of Photosynthesis, the chlorophyll will be activated by light. Water molecule is split to release H+ ions and also oxygen.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is it important for light dependent reactions to separate water?
- Q. What are the steps in the light reactions?
- Q. What are the three steps of light reactions?
- Q. What are the three parts of the light dependent reactions?
- Q. What are the two things needed for light-dependent reactions?
- Q. Do light-dependent reactions produce oxygen?
- Q. What is the primary function of light-dependent reactions?
- Q. How important is light dependent reaction to our ecosystem?
- Q. What is the primary function of the light reactions of photosynthesis quizlet?
- Q. What is the primary function of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis Quizizz?
- Q. What is the primary function of cyclic electron flow?
- Q. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
- Q. What is another name for light-independent reactions?
- Q. What are light dependent and independent reactions?
- Q. How do light and dark reactions work together?
- Q. Why do the disks float when the light is on?
- Q. What materials are needed for light reactions?
- Q. What raw materials are used in light dependent reactions?
- Q. What are the materials needed for cellular respiration?
- Q. What are the raw materials of dark reactions?
- Q. Is oxygen released in light or dark reactions?
- Q. What is a dark reaction?
Q. What are the steps in the light reactions?
Here are the basic steps:
- Light absorption in PSII. When light is absorbed by one of the many pigments in photosystem II, energy is passed inward from pigment to pigment until it reaches the reaction center.
- ATP synthesis.
- Light absorption in PSI.
- NADPH formation.
- (1st Time) Energy is absorbed from the sun.
- Water is broken down.
- Hydrogen ions are transported across the thylakoid membrane.
- (2nd Time) Energy is absorbed from the sun.
- NADPH is produced from NADP+.
- Hydrogen ions diffuse through the protein channel.
- ADP becomes ATP.
Q. What are the three steps of light reactions?
The light-independent reactions of the Calvin cycle can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
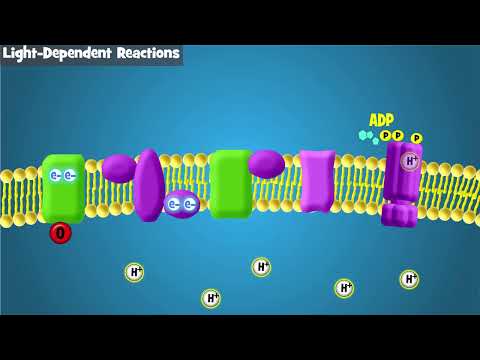
Q. What are the three parts of the light dependent reactions?
4 Cards in this Set
| What are the three parts of the light-dependent reactions? | Photosystem 2, Photosystem 1, and ATP Synthase |
|---|---|
| What are the functions of photosynthesis 1? | to absorb and transfer energy when it goes into the electron transport chain. also to break down water as it goes across the thylakoid membrane. |
Q. What are the two things needed for light-dependent reactions?
What two things are needed for the light-dependent reactions to take place? -Water and light are needed for light-dependent reactions.
Q. Do light-dependent reactions produce oxygen?
In the light-dependent reactions, which take place at the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight and then converts it into chemical energy with the use of water. The light-dependent reactions release oxygen as a byproduct as water is broken apart.
Q. What is the primary function of light-dependent reactions?
The overall function of light-dependent reactions, the first stage of photosynthesis, is to convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP, which are used in light-independent reactions and fuel the assembly of sugar molecules.
Q. How important is light dependent reaction to our ecosystem?
Although photosynthesis is most commonly associated with plants, microbial photosynthesis is also a significant supplier of chemical energy, fueling many diverse ecosystems. 1: The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis (left) convert light energy into chemical energy, forming ATP and NADPH.
Q. What is the primary function of the light reactions of photosynthesis quizlet?
The primary function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is to: produce energy-rich ATP and NADPH.
Q. What is the primary function of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis Quizizz?
Photosynthesis converts radiant energy into chemical energy.
Q. What is the primary function of cyclic electron flow?
In higher plants, the generation of proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane (ΔpH) through cyclic electron flow (CEF) has mainly two functions: (1) to generate ATP and balance the ATP/NADPH energy budget, and (2) to protect photosystems I and II against photoinhibition.
Q. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions?
The products of the light-dependent reactions, ATP and NADPH, are both required for the endergonic light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reactions involve two photosystems called Photosystem I and Photosystem II.
Q. What is another name for light-independent reactions?
Calvin-Benson cycle
Q. What are light dependent and independent reactions?
In the light-independent reactions or Calvin cycle, the energized electrons from the light-dependent reactions provide the energy to form carbohydrates from carbon dioxide molecules. In addition, several enzymes of the light-independent reactions are activated by light.
Q. How do light and dark reactions work together?
Light and dark reactions in photosynthesis Light-independent reactions (dark reactions). Light reactions need light to produce organic energy molecules (ATP and NADPH). They are initiated by colored pigments, mainly green colored chlorophylls. Dark reactions make use of these organic energy molecules (ATP and NADPH).
Q. Why do the disks float when the light is on?
The leaf disks intake carbon dioxide from a baking soda solution and sink to the bottom of a cup of water. When exposed to light, the disks use carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen and glucose. Oxygen released from the leaves forms tiny bubbles that cause the leaves to float.
Q. What materials are needed for light reactions?
The reactants of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. These are the molecules necessary to begin the process. But one more item is necessary, and that is sunlight. All three components, carbon dioxide, water, and the sun’s energy are necessary for photosynthesis to occur.
Q. What raw materials are used in light dependent reactions?
CO2, water, light, and chlorophyll are the raw materials for photosynthesis. But, in case of light dependent reaction or light reaction of photosynthesis, it is most influenced by presence or absence of light.
Q. What are the materials needed for cellular respiration?
Oxygen and glucose are both reactants in the process of cellular respiration. The main product of cellular respiration is ATP; waste products include carbon dioxide and water.
Q. What are the raw materials of dark reactions?
What is a dark reaction? In the dark reaction, plants use carbon dioxide with ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to produce glucose. It takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast.
Q. Is oxygen released in light or dark reactions?
The light reaction takes place in the thylakoid discs. There, water (H20) is oxidized, and oxygen (O2) is released. The electrons freed up from water are transfered to ATP and NADPH. The dark reaction occurs outside of the thylakoids.
Q. What is a dark reaction?
: any of a series of chemical reactions in photosynthesis not requiring the presence of light and involving the reduction of carbon dioxide to form carbohydrate especially : calvin cycle.