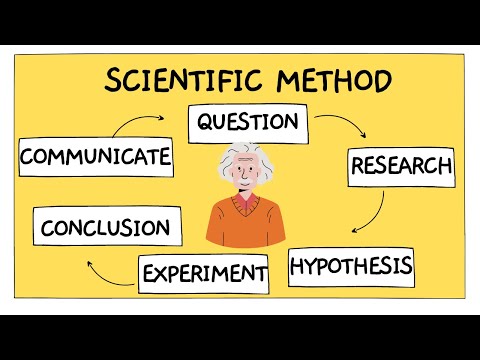
The five components of the scientific method are: observations, questions, hypothesis, methods and results.
Q. How do scientists conduct research?
When conducting research, scientists use the scientific method to collect measurable, empirical evidence in an experiment related to a hypothesis (often in the form of an if/then statement), the results aiming to support or contradict a theory.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do scientists conduct research?
- Q. What is the main reason for scientific investigations?
- Q. Why do scientists conduct research after they ask a question?
- Q. What are the 3 principles of scientific thinking?
- Q. Does the scientific method always reveal the truth?
- Q. What are the 7 global challenges?
- Q. Which is the biggest challenge before the world?
- Q. What is the biggest problem facing humanity today?
- Q. What is the problem with humanity?
- Q. What wrong with the world Dear Sir I am?
- Q. What are some problems in the World 2021?
- Q. What challenges do governments face?
- Q. What does a scientist conduct?
- Q. Why is it important for scientist to conduct experiments for their investigations?
- Q. What is the scientific thinking?
- Q. Who are the scientific thinkers?
- Q. What are the six principles of scientific thinking?
- Q. What is an example of scientific reasoning?
- Q. What type of reasoning is the scientific method?
- Q. What are the 2 types of inductive arguments?
- Q. What is a good inductive argument?
- Q. What are the two kinds of deductive arguments?
- Q. What does deductive mean?
- Q. What is deductive example?
- Q. What is the meaning of deductive method?
- Q. What is inductive and deductive reasoning?
- Q. What best describes the deductive approach?
- Q. How do you do deductive reasoning?
- Q. Does deductive reasoning use facts?
- Q. Why is deductive reasoning important?
- Q. What jobs use deductive reasoning?
- Q. What is the importance of deductive and inductive reasoning?
- Q. What is inductive method of teaching?
Q. What is the main reason for scientific investigations?
Scientists conduct investigations for all kinds of reasons. They may want to explore new ideas, gather evidence or prove or disprove previous results. Although scientists must follow certain methods to ensure their results are fair and accurate, there are many ways they can conduct an investigation.
Q. Why do scientists conduct research after they ask a question?
Publishing results of research projects in peer-reviewed journals enables the scientific and medical community to evaluate the findings themselves. It also provides instructions so that other researchers can repeat the experiment or build on it to verify and confirm the results.
Q. What are the 3 principles of scientific thinking?
The scientific method is practiced within a context of scientific thinking, and scientific (and critical) thinking is based on three things: using empirical evidence (empiricism), practicing logical reasonsing (rationalism), and possessing a skeptical attitude (skepticism) about presumed knowledge that leads to self- …
Q. Does the scientific method always reveal the truth?
The scientific method is very simple – a basic “crap detector” if you will. The strength of the scientific method is found not so much in its ability to detect truth, but in its ability to detect error. It has the ability to rule out those hypothesis and theories that are definitely wrong.
Q. What are the 7 global challenges?
The Seven Revolutions framework identifies the following seven global trends—or global challenges—as likely to transform the world over the next several decades:
- Population.
- Resources.
- Technology.
- Information.
- Economies.
- Conflict.
- Governance.
Q. Which is the biggest challenge before the world?
Explanation:
- Poverty.
- Unemployment.
- Terrorism.
- Environmental issues.
- Rasicsm.
Q. What is the biggest problem facing humanity today?
The Biggest Global Issues Facing Mankind
- Food and Malnutrition.
- Access to Clean Water.
- Refugee Crisis.
- AIDS Epidemic.
- Eradicating Poverty.
Q. What is the problem with humanity?
War, contagious diseases,and overpopulation. All of these lead to environmental degradation, poor nutrition and pollution. If a solution is not found quickly, these problems caused by the human race will cause humanity’s end.
Q. What wrong with the world Dear Sir I am?
There is an anecdote often told of G.K. Chesterton, an English author and philosopher. Around 1910, the London Times requested essays responding to the prompt, “What is wrong with the world (1)?” Chesterton’s response was brief: “Dear Sirs, I am. I am what is wrong with the world.
Q. What are some problems in the World 2021?
5 Global Crises the world can’t ignore in 2021
- In some of the world’s most dangerous and complex places, COVID-19 has reversed decades of progress, with the aftershocks of the pandemic threatening more children’s lives than the virus itself.
- Refugees.
- Climate Change.
- Child Marriage/Gender Discrimination.
Q. What challenges do governments face?
Although the challenges governments face are nearly universal, how leaders go about tackling them might vary significantly, depending on the government structure and ideology….Six pressing challenges
- Economy.
- Healthcare.
- Education.
- National safety and security.
- Climate.
- Trust in government.
Q. What does a scientist conduct?
Scientific research is the research performed by applying systematic and constructed scientific methods to obtain, analyze, and interpret data. Hypothesis should be clear, specific, and directly aim to answer the research question. A strong and testable hypothesis is the fundamental part of the scientific research.
Q. Why is it important for scientist to conduct experiments for their investigations?
Scientific investigations produce evidence that helps answer questions and solve problems. If the evidence cannot provide answers or solutions, it may still be useful. It may lead to new questions or problems for investigation. As more knowledge is discovered, science advances.
Q. What is the scientific thinking?
Scientific thinking refers to both thinking about the content of science and the set of reasoning processes that permeate the field of science: induction, deduction, experimental design, causal reasoning, concept formation, hypothesis testing, and so on.
Q. Who are the scientific thinkers?
Top 13 Important Thinkers in The Scientific Revolution
- Giordano Bruno (1548–1600)
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632–1723)
- William Harvey (1578–1657)
- Robert Boyle (1627–1691)
- Paracelsus (1493–1541)
- Tycho Brahe (1546–1601)
- Johannes Kepler (1571–1630)
- Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543)
Q. What are the six principles of scientific thinking?
The Six Principles of Scientific Thinking.
- Extraordinary Claims tells us that extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence.
- Falsifiability.
- Occam’s Razor (Also called the “principle of parsimony”).
- Replicability.
- Ruling Out Rival Hypotheses.
- Correlation vs.
Q. What is an example of scientific reasoning?
For example, we know that all organisms are made of cells and need to maintain homeostasis and must reproduce to stay alive. Therefore, since humans are organisms, we can then deduce that humans are made of cells, maintain homeostasis and reproduce. Deductions are based on valid reasoning.
Q. What type of reasoning is the scientific method?
Inductive reasoning has its place in the scientific method. Scientists use it to form hypotheses and theories. Deductive reasoning allows them to apply the theories to specific situations.
Q. What are the 2 types of inductive arguments?
There are a few key types of inductive reasoning.
- Generalized. This is the simple example given above, with the white swans.
- Statistical. This form uses statistics based on a large and random sample set, and its quantifiable nature makes the conclusions stronger.
- Bayesian.
- Analogical.
- Predictive.
- Causal inference.
Q. What is a good inductive argument?
An inductive argument is an argument that is intended by the arguer to be strong enough that, if the premises were to be true, then it would be unlikely that the conclusion is false. For example, this is a reasonably strong inductive argument: Today, John said he likes Romona.
Q. What are the two kinds of deductive arguments?
There are three common types of deductive reasoning:
- Syllogism.
- Modus ponens.
- Modus tollens.
Q. What does deductive mean?
1 : of, relating to, or provable by deriving conclusions by reasoning : of, relating to, or provable by deduction (see deduction sense 2a) deductive principles. 2 : employing deduction in reasoning conclusions based on deductive logic.
Q. What is deductive example?
Examples of deductive logic: Joe is a man. Therefore Joe is mortal. If the first two statements are true, then the conclusion must be true. Bachelors are unmarried men. Bill is unmarried.
Q. What is the meaning of deductive method?
Deductive reasoning, also deductive logic, is the process of reasoning from one or more statements (premises) to reach a logical conclusion. If all premises are true, the terms are clear, and the rules of deductive logic are followed, then the conclusion reached is necessarily true.
Q. What is inductive and deductive reasoning?
The main difference between inductive and deductive reasoning is that inductive reasoning aims at developing a theory while deductive reasoning aims at testing an existing theory. Inductive reasoning moves from specific observations to broad generalizations, and deductive reasoning the other way around.
Q. What best describes the deductive approach?
Deductive reasoning is a type of logical thinking that starts with a general idea and reaches a specific conclusion. It’s sometimes is referred to as top-down thinking or moving from the general to the specific. Learn more about deductive reasoning and its value in the workplace.
Q. How do you do deductive reasoning?
The process of deductive reasoning includes the following steps:
- Initial assumption. Deductive reasoning begins with an assumption.
- Second premise. A second premise is made in relation to the first assumption.
- Testing. Next, the deductive assumption is tested in a variety of scenarios.
- Conclusion.
Q. Does deductive reasoning use facts?
Industive reasoning uses reason, and patterns to come to a conclusion about something, while deductive reasoning uses facts, logic, and definitions to come to a conclusion about something.
Q. Why is deductive reasoning important?
Deductive reasoning is an important skill that can help you think logically and make meaningful decisions in the workplace. This mental tool enables professionals to come to conclusions based on premises assumed to be true or by taking a general assumption and turning it into a more specific idea or action.
Q. What jobs use deductive reasoning?
What does Deductive Reasoning mean?
- Neuropsychologists and Clinical Neuropsychologists.
- Anesthesiologists.
- Judges, Magistrate Judges, and Magistrates.
- Air Traffic Controllers.
- Dentists, General.
- Biostatisticians.
- Surgeons.
- Hospitalists.
Q. What is the importance of deductive and inductive reasoning?
With deductive reasoning, you start with a generalization or theory and then test it by applying it to specific incidents. Deductive reasoning is using general ideas to reach a specific conclusion. Inductive reasoning uses specific ideas to reach a broad conclusion.
Q. What is inductive method of teaching?
Meaning: The inductive method of teaching means that the teacher presents the rule through situations and sentences and does guided practice, then the learners do free practice. After that, the teacher deduces or elicits the rule form from the learners themselves by themselves.