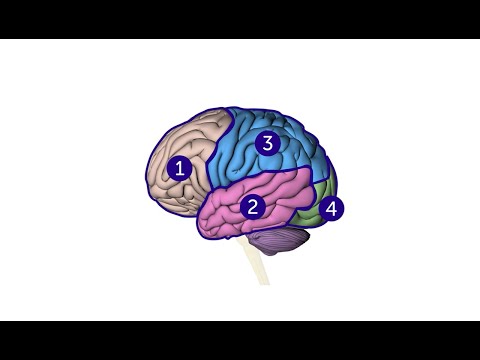
Each brain hemisphere (parts of the cerebrum) has four sections, called lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital.
Q. What structure in the developing embryo becomes the brain?
neural tube
Table of Contents
- Q. What structure in the developing embryo becomes the brain?
- Q. What are brain divisions?
- Q. What are the three brain regions during embryonic development?
- Q. What is the order of embryonic brain development?
- Q. How is the human brain divided?
- Q. Does the brain feel pain?
- Q. Which organs in the cell works like brain?
- Q. What are the 3 brains?
- Q. Do brain cells grow back?
- Q. Why is the brain so soft?
- Q. What does human brain taste like?
- Q. Is a brain solid?
- Q. What do brains really look like?
- Q. Can you live without a brain?
- Q. Why do zombies eat brains?
- Q. Do brains smell?
- Q. Why is smell so powerful?
- Q. What does sad smell like?
- Q. Why do I smell trigger memories?
- Q. What can trigger memories?
- Q. Can you smell memories?
- Q. Why are smells so nostalgic?
- Q. Do scents bring back memories?
- Q. How do smells affect the brain?
- Q. Is nostalgia a good or bad feeling?
- Q. What does Anemoia mean?
- Q. Why does nostalgia make me happy?
- Q. Why nostalgia is bad for you?
Q. What are brain divisions?
The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.
Q. What are the three brain regions during embryonic development?
One way of thinking about how the brain is arranged is to use these three regions—forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain—which are based on the primary vesicle stage of development (Figure 14.1. 2a).
Q. What is the order of embryonic brain development?
The Structure of the Brain As the fetus develops, the grooves and folds in the neural tube deepen, giving rise to different layers of the brain. The human brain is split up into three major layers: the hindbrain, the midbrain, and the forebrain.
Q. How is the human brain divided?
The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain. The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum (1). The hindbrain controls the body’s vital functions such as respiration and heart rate.
Q. Does the brain feel pain?
The brain itself does not feel pain because there are no nociceptors located in brain tissue itself. This feature explains why neurosurgeons can operate on brain tissue without causing a patient discomfort, and, in some cases, can even perform surgery while the patient is awake.
Q. Which organs in the cell works like brain?
It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate’s body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion….Primates.
| Species | EQ |
|---|---|
| Rat | 0.4 |
Q. What are the 3 brains?
You have three brains – your HEAD brain, your HEART brain, and your GUT brain….The Role of the Three Brains
- The head brain analyzes information and applies logic.
- The heart brain senses the world through emotion and feelings.
- The gut brain is used for understanding our identity and who we are in the world.
Q. Do brain cells grow back?
Summary: When adult brain cells are injured, they revert to an embryonic state, say researchers. In their newly adopted immature state, the cells become capable of re-growing new connections that, under the right conditions, can help to restore lost function.
Q. Why is the brain so soft?
Brains are so soft to the touch that, in order to stay safe, your brain actually floats inside your skull in a sea of cerebrospinal fluid, separated from contact with the bone. If nothing else, seeing this really does help make sense of the roughly 1.2 million concussions we see in the U.S. each year.
Q. What does human brain taste like?
Both brains and sweetbreads possess animalistic flavor that’s neither iron-intensive like the livers or gamey like the kidneys. Brains also taste somewhat like a firm fish roe, though without the fishiness, of course.
Q. Is a brain solid?
The brain is neither a solid nor a liquid. The mechanical response of the brain to external loads is strain-rate dependent.
Q. What do brains really look like?
Human Brain Tissue Your brain is the size of a large grapefruit, but it looks like a large pinkish-gray walnut. There are many folds and creases and it feels soft and squishy. It weighs about 1 pound at birth, 2 pounds at elementary age, and 3 pounds as an adult.
Q. Can you live without a brain?
Since it controls vital functions such as breathing, swallowing, digestion, eye movement and heartbeat, there can be no life without it. But the rest of the brain is obviously capable of some remarkable feats, with one part able to compensate for deficiencies in another.
Q. Why do zombies eat brains?
In regards to why the zombies feed on brains, the closest we’ve ever come to an official explanation is a quote from Return of the Living Dead’s writer and director, Dan O’Bannon, who suggested that the undead felt the need to feed on the brains of the recently living because it somehow made them feel better byeasing …
Q. Do brains smell?
When stimulated by a chemical with a smell, or an odorant, they send nerve impulses to thousands of clusters of neurons in the glomeruli, which make up the olfactory bulb, the brain’s smell center. Different patterns of glomerular activation are known to generate the sensation of specific odors.
Q. Why is smell so powerful?
Why indeed smell is so powerful? One reason is that olfactory system is located in the same part of our brain that effects emotions, memory, and creativity. And, that part of the brain processes smell, interacts with regions of the brain that are responsible for storing emotional memories.
Q. What does sad smell like?
Food science geek. Originally Answered: What does sadness smell and taste like? Sadness smells like a well done steak. Like an extra well done steak.
Q. Why do I smell trigger memories?
Scents bypass the thalamus and go straight to the brain’s smell center, known as the olfactory bulb. The olfactory bulb is directly connected to the amygdala and hippocampus, which might explain why the smell of something can so immediately trigger a detailed memory or even intense emotion.
Q. What can trigger memories?
When a particular stimulus—a situation, an event, a person, or a thought—activates an emotional memory, it can be enjoyable or painful, although it may not be felt as intensely as the original experience of the emotion. A specific date, for example, may trigger emotional memories.
Q. Can you smell memories?
Smell and Memory The sense of smell is closely linked with memory, probably more so than any of our other senses. Those with full olfactory function may be able to think of smells that evoke particular memories; the scent of an orchard in blossom conjuring up recollections of a childhood picnic, for example.
Q. Why are smells so nostalgic?
“Olfactory has a strong input into the amygdala, which process emotions. The kind of memories that it evokes are good and they are more powerful,” explains Eichenbaum. This close relationship between the olfactory and the amygdala is one of the reason odors cause a spark of nostalgia.
Q. Do scents bring back memories?
Scents are “really special” because “they can bring back memories that might otherwise never be recalled,” Herz said. Typically, when a person smells something that’s connected to a meaningful event in their past, they will first have an emotional response to the sensation and then a memory might follow.
Q. How do smells affect the brain?
Smells are handled by the olfactory bulb, the structure in the front of the brain that sends information to the other areas of the body’s central command for further processing. Odors take a direct route to the limbic system, including the amygdala and the hippocampus, the regions related to emotion and memory.
Q. Is nostalgia a good or bad feeling?
Recently scientists have explored the bittersweet feeling of nostalgia, finding that it serves a positive function, improving mood and possibly mental health. But here they found that nostalgia boosted self-continuity by increasing a sense of social connectedness.
Q. What does Anemoia mean?
Anemoia is a word coined by The Dictionary of Obscure Sorrows, which means: nostalgia for a time you’ve never known. I believe that at our core, we all are deeply desiring of a world where justice and liberation dominate our social fabric. A time we have not yet seen, yet inherently yearn for.
Q. Why does nostalgia make me happy?
Because nostalgia is both an emotion and a thought process, it’s considered a blended emotion and different than other emotions. For instance, when you’re happy, you can simply be happy, but when you’re nostalgic it involves the cognitive process of remembering, which also has emotions attached to it.
Q. Why nostalgia is bad for you?
We miss and long for something before it’s even over, and it leads to sadness, worry, and anxiety. An American study released in 2020 shows that, as well as affecting our reaction, poorly timed nostalgia can also affect our ability to learn from our reminiscing.