Characteristics of Uniform Circular Motion (U.C.M.)
Q. What keeps the object moving in circular path?
A centripetal force is a net force that acts on an object to keep it moving along a circular path. Newton’s 1ˢᵗ law tells us that an object will continue moving along a straight path unless acted on by an external force. The external force here is the centripetal force.
Table of Contents
- Q. What keeps the object moving in circular path?
- Q. What is the characteristics of uniform circular motion?
- Q. What is kinematic circular motion?
- Q. What is an example of rotational motion?
- Q. What is the example of rotary motion?
- Q. What is a position vector in circular motion?
- Q. What is the symbol of centripetal acceleration?
- Q. Is there displacement in circular motion?
- Q. Why is displacement zero in a circular motion?
- Q. How much is the displacement in one cycle of circular motion?
- Q. What is the difference between linear and angular displacement?
- Q. What is relation between linear and angular velocity?
- Q. What is the relation between linear and angular acceleration?
- Q. What is the relation between linear and angular momentum?
- Q. What is angular momentum equal to?
- Q. Which kind of vector is angular momentum?
- Q. Why is angular momentum conserved?
Q. What is the characteristics of uniform circular motion?
In physics, uniform circular motion describes the motion of a body traversing a circular path at constant speed. Since the body describes circular motion, its distance from the axis of rotation remains constant at all times.
- The angular velocity is constant (ω = cst)
- The velocity vector is tangent to the trajectory at each point and its direction is the same as the direction of the motion.
- Both, the angular acceleration (α) and tangential acceleration (at) are zero, since the speed (the velocity vector magnitude) is constant.
Q. What is kinematic circular motion?
In circular motion the direction of motion is tangential and always changing, but the speed is constant. The force required to change the velocity (and accelerate the object) is always towards the centre of the circle and perpendicular to the motion. The resultant force and hence the acceleration is towards the centre.
Q. What is an example of rotational motion?
Rotational motion Examples Motion of wheel, gears, motors, etc is rotational motion. Motion of the blades of the helicopter is also rotatory motion. A door, swiveling on its hinges as you open or close it. A spinning top, motion of a Ferris Wheal in an amusement park.
Q. What is the example of rotary motion?
Answer: The five examples of rotary motion are electric fan, earths rotation, spinning knob, turbine and bicycle wheels. Explanation: The rotatory motion is a form of motion where the subject moves in a circular path with rotation around an axis which is an imaginary axis.
Q. What is a position vector in circular motion?
A particle executing circular motion can be described by its position vector →r(t). As the particle moves on the circle, its position vector sweeps out the angle θ with the x-axis. Vector →r(t) making an angle θ with the x-axis is shown with its components along the x- and y-axes.
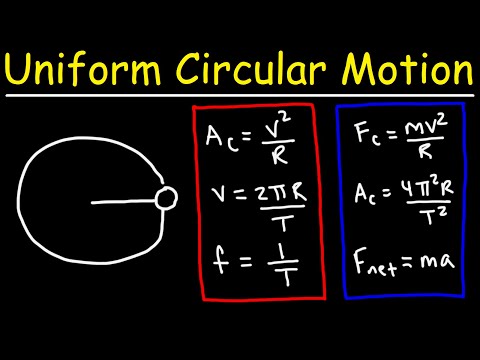
Q. What is the symbol of centripetal acceleration?
Equations
| Equation | Symbol breakdown |
|---|---|
| a c = v 2 r a_c = /dfrac{v^2}{r} ac=rv2 | a c a_c aca, start subscript, c, end subscript is radial acceleration, v is linear speed, and r is radius of the circle |
Q. Is there displacement in circular motion?
In the case of linear motion, the difference between the initial point and final point is termed as displacement. Thus the circular motion equivalence of displacement is Angular displacement and is represented using Greek letter θ.
Q. Why is displacement zero in a circular motion?
For the work done we need component of force along the direction of displacement but displacement and force are 90°, at each and every point on the circular track and therefore the component of force along the direction of displacement will always be zero in case of a body moving in a circular track or a body …
Q. How much is the displacement in one cycle of circular motion?
From the definition, it is clear that displacement to be considered is in between only one point, which turns out to be zero. Therefore, we can come to the conclusion that the displacement in one cycle of a circular motion is zero.
Q. What is the difference between linear and angular displacement?
The angular displacement is not a length (not measured in meters or feet), so an angular displacement is different than a linear displacement. As the object rotates through the angular displacement phi, the point on the edge of the disk moves distance sa along a circular path.
Q. What is relation between linear and angular velocity?
Relation Between Linear Velocity and Angular Velocity ⇒ |v| = rω, which is the ‘relation between linear and angular velocity. As the particle starts moving away from the center, the linear velocity starts increasing. It is maximum at the circumference of the circle.
Q. What is the relation between linear and angular acceleration?
α=atr. These equations mean that linear acceleration and angular acceleration are directly proportional. The greater the angular acceleration is, the larger the linear (tangential) acceleration is, and vice versa.
Q. What is the relation between linear and angular momentum?
Angular momentum of an object with linear momentum is proportional to mass, linear velocity, and perpendicular radius from an axis to the line of the object’s motion. Δ L /Delta L ΔL is change of angular momentum, τ is net torque, and Δ t /Delta t Δt is time interval.
Q. What is angular momentum equal to?
The magnitude of the angular momentum of an orbiting object is equal to its linear momentum (product of its mass m and linear velocity v) times the perpendicular distance r from the centre of rotation to a line drawn in the direction of its instantaneous motion and passing through the object’s centre of gravity, or …
Q. Which kind of vector is angular momentum?
First, the L vector represents the angular momentum—yes, it’s a vector. Second, the r vector is a distance vector from some point to the object and finally the p vector represents the momentum (product of mass and velocity).
Q. Why is angular momentum conserved?
Objects can change their shape and still conserve angular momentum. Angular momentum depends on the rotational velocity of an object, but also its rotational inertia. Since there is no external net torque on the ice skater, her angular momentum remains constant because her angular velocity magnitude increases.