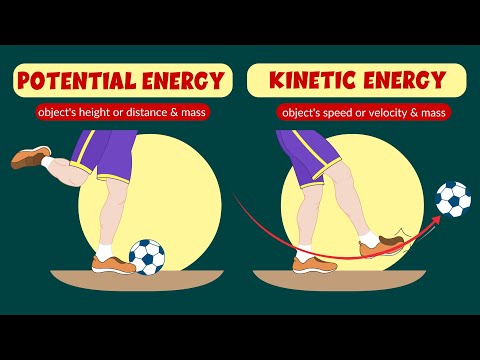
Gravitational Potential Energy is determined by three factors: mass, gravity, and height. All three factors are directly proportional to energy.
Q. What are examples of elastic potential energy?
Many objects are designed specifically to store elastic potential energy, for example:
Table of Contents
- Q. What are examples of elastic potential energy?
- Q. Which is the best example of potential energy?
- Q. What does not affect an object’s potential energy?
- Q. What is the relationship of mass weight and height to the PE of an object?
- Q. Why does potential energy increase with height?
- Q. Does potential energy increase with heat?
- Q. Does potential energy increase with distance?
- Q. Can you cite situations which show the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
- Q. What type of energy do humans need?
- Q. What is energy and its types?
- Q. What is energy and its unit?
- Q. What is energy made up of?
- Q. What is energy in simple words?
- Q. What is elastic potential energy equal to?
- Q. What are the factors of elastic potential energy?
- Q. Is elastic potential energy always positive?
- Q. What is the difference between elastic potential energy and GPE?
- Q. Is elastic potential energy dependent on mass?
- Q. Is elastic potential energy?
- Q. Why elastic potential energy is positive?
- The coil spring of a wind-up clock.
- An archer’s stretched bow.
- A bent diving board, just before a divers jump.
- The twisted rubber band which powers a toy airplane.
- A bouncy ball, compressed at the moment it bounces off a brick wall.
Q. Which is the best example of potential energy?
Potential energy is the stored energy an object has because of its position or state. A bicycle on top of a hill, a book held over your head, and a stretched spring all have potential energy.
Q. What does not affect an object’s potential energy?
so it is independent of the speed of object. So speed of object will not affect the gravitational potential energy.
Q. What is the relationship of mass weight and height to the PE of an object?
PEgrav = m *• g • h In the above equation, m represents the mass of the object, h represents the height of the object and g represents the gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg on Earth) – sometimes referred to as the acceleration of gravity.
Q. Why does potential energy increase with height?
Since the gravitational potential energy of an object is directly proportional to its height above the zero position, a doubling of the height will result in a doubling of the gravitational potential energy.
Q. Does potential energy increase with heat?
Yes, potential energy increases with increasing temperature for at least the following three reasons: At a higher temperature, more atoms/molecules are in excited electronic states. Higher electronic states correspond to greater potential energy. Potential Energy is -2 times Kinetic Energy.
Q. Does potential energy increase with distance?
Gravitational potential energy at large distances is directly proportional to the masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them. The gravitational potential energy increases as r increases.
Q. Can you cite situations which show the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
When an object is at rest, the body is said to possess potential energy. In another case, when the object is in motion, then it is said to possess kinetic energy. When the rock falls, it possesses kinetic energy. The energy which is stored in a body because of the elevation is called gravitational potential energy.
Q. What type of energy do humans need?
Like an automobile only runs on gasoline, the human body runs on only one kind of energy: chemical energy. More specifically, the body can use only one specific form of chemical energy, or fuel, to do biological work – adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Q. What is energy and its types?
Energy, in physics, the capacity for doing work. It may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work—i.e., energy in the process of transfer from one body to another.
Q. What is energy and its unit?
Energy is the capacity of a physical system to do work. The common symbol for energy is the uppercase letter E. The standard unit is the joule, symbolized by J. One joule (1 J) is the energy resulting from the equivalent of one newton (1 N) of force acting over one meter (1 m) of displacement.
Q. What is energy made up of?
Common forms of energy include solid mass or as non-solid matter, such as heat, light, electrical, sound, gravitational, potential (stored energy) and kinetic (energy of motion). Quantum physics states that mass and energy are interchangeable, and consequently that mass is merely a manifestation of energy.
Q. What is energy in simple words?
The simplest definition of energy is “the ability to do work”. Energy is how things change and move. It takes energy to cook food, to drive to school, and to jump in the air. Different forms of Energy. Energy can take a number of different forms.
Q. What is elastic potential energy equal to?
Elastic potential energy is Potential energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, such as the stretching of a spring. It is equal to the work done to stretch the spring, which depends upon the spring constant k as well as the distance stretched.
Q. What are the factors of elastic potential energy?
Several factors determine how much elastic potential energy an object has stored. One factor is the material the object is made of. Some materials, like rubber, readily return to their original shape after being deformed. A second factor that affects elastic potential energy is the amount of deformation.
Q. Is elastic potential energy always positive?
Although the spring force is a restoring force and has a negative sign, the elastic potential energy U s U_s UsU, start subscript, s, end subscript cannot be negative. As soon as the spring is stretched or compressed, there is positive potential energy stored in the spring.
Q. What is the difference between elastic potential energy and GPE?
Gravitational potential energy is energy in an object that is held in a vertical position. Elastic potential energy is energy stored in objects that can be stretched or compressed.
Q. Is elastic potential energy dependent on mass?
Things with kinetic energy can do work. Kinetic energy depends on an object’s mass and velocity. It includes gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Gravitational potential energy depends on an object’s weight and height above the ground.
Q. Is elastic potential energy?
What is elastic energy? Elastic energy is a form of potential energy, because it is stored in the bonds between atoms in an object or substance when it is temporarily under stress. This stress could be due to the object being stretched or squashed.
Q. Why elastic potential energy is positive?
So, the motion involves net increase of potential energy whether it is being compressed or elongated. Hence, in that sense, change in potential energy is always positive, in this case, as John Rennie has mentioned in his post.