High-Performance Liquid Chromatography These machines help forensic scientists analyze volatile substances such as gunpowder residue, fibers, and toxins. One of its most common uses is to determine materials used in explosives. Additionally, many explosive materials can wear down during the gas chromatography methods.
Q. How does chromatography used in forensic science?
In forensics, police use chromatography to identify and analyze substances found at a crime scene. Every mixture is made up of molecules of different chemicals, in varying amounts. Chromatography works by separating the chemicals out of a mixture and studying how the molecules behave during the separation process.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does chromatography used in forensic science?
- Q. How is chromatography used in a crime scene?
- Q. Why do scientists use chromatography?
- Q. What are 3 uses of chromatography?
- Q. What is the basic principle of chromatographic process?
- Q. What are the 4 types of chromatography?
- Q. What is chromatographic technique?
- Q. What is the principle of TLC?
- Q. What is TLC used for?
- Q. What are the advantages of TLC?
- Q. Why silica gel is used in TLC?
- Q. How long should you run a TLC plate for?
- Q. Is silica gel more polar than water?
- Q. Is silica polar or nonpolar?
- Q. Why is silica so polar?
- Q. Is benzene polar or nonpolar?
- Q. Is silica gel on a TLC plate polar or non polar?
- Q. Do more polar solvents elute faster?
- Q. Does a higher Rf value mean more polar?
Q. How is chromatography used in a crime scene?
Separation of complex mixtures (known as chromatography) is an essential tool in forensic science. It is routinely used to identify and compare samples of drugs, explosives, inks and biological samples such as saliva, urine, blood and other.
Q. Why do scientists use chromatography?
Chromatography is a method used by scientists for separating organic and inorganic compounds so that they can be analyzed and studied. By analyzing a compound, a scientist can figure out what makes up that compound. Chromatography is a great physical method for observing mixtures and solvents.
Q. What are 3 uses of chromatography?
5 Everyday uses for Chromatography
- Creating vaccinations. Chromatography is useful in determining which antibodies fight various diseases and viruses.
- Food testing.
- Beverage testing.
- Drug testing.
- Forensic testing.
Q. What is the basic principle of chromatographic process?
Chromatography is based on the principle where molecules in mixture applied onto the surface or into the solid, and fluid stationary phase (stable phase) is separating from each other while moving with the aid of a mobile phase.
Q. What are the 4 types of chromatography?
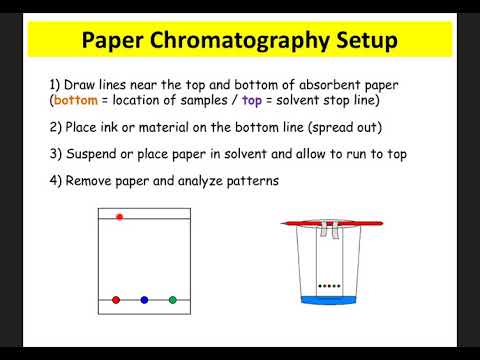
While this method is so accurate, there are primarily four different types of chromatography: gas chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, thin-layer chromatography, and paper chromatography.
Q. What is chromatographic technique?
Chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid (gas, solvent, water.) called the mobile phase, which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which is fixed a material called the stationary phase.
Q. What is the principle of TLC?
What is the principle of TLC? TCL is based on the principle of separation through adsorption type. The separation relies on the relative empathy of compounds towards the mobile phase and stationary phase.
Q. What is TLC used for?
TLC is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography can be used to monitor the progress of a reaction, identify compounds present in a given mixture, and determine the purity of a substance.
Q. What are the advantages of TLC?
Advantages of TLC include rapid analysis time because many samples can be analyzed simultaneously, low solvent usage on a per-sample basis, a high degree of accuracy and precision for instrumental TLC, and sensitivity in the nanogram or picogram range.
Q. Why silica gel is used in TLC?
Silica gel is by far the most widely used adsorbent and remains the dominant stationary phase for TLC. The surface of silica gel with the highest concentration of geminal and associated silanols is favored most for the chromatography of basic compounds because these silanols are less acidic.
Q. How long should you run a TLC plate for?
Transcribed image text: How long should you run a TLC plate for? Until the solvent front is about half way up. Until the solvent front is at the top of the plate. 2 minutes.
Q. Is silica gel more polar than water?
In general, good separation is achieved by using fairly polar stationary phases and low polarity mobile phases such as hexane. Water, it should be noted, is a very polar solvent. Silica gel is less polar than alumina and is an acidic adsorbent, thus preferentially retaining basic compounds.
Q. Is silica polar or nonpolar?
Silica gel is a polar adsorbent. This allows it to preferentially adsorb other polar materials. When it comes to polarity, materials interact more with like materials. This principle is particularly important to many laboratories, which use silica gel as the stationary phase for column chromatography separations.
Q. Why is silica so polar?
Silica gel, the most commonly used stationary phase, has the empirical formula SiO2. However, at the surface of the silica gel particles, the dangling oxygen atoms are bound to protons. The presence of these hydroxyl groups renders the surface of silica gel highly polar.
Q. Is benzene polar or nonpolar?
In case of benzene, it is a non polar molecule because it contains only C-H and C-C bonds. Since carbon is slightly more electronegative than H , a C-H bond is very slightly polar and has a very small dipole moment.
Q. Is silica gel on a TLC plate polar or non polar?
It should be noted that silica gel is highly polar and is capable of hydrogen bonding. Consider the side-on view of the development of a TLC plate below. As the solvent travels up the plate, over the spot, an equilibrium is set up, as development solvent competes with the TLC plate for the solute.
Q. Do more polar solvents elute faster?
Note that the more polar the solvent, the faster compounds elute, regardless of the compounds polarity. This will force compounds into the mobile phase, and result in faster elution/increased travel distance. It may also be helpful to remember that alumina and silica are much more polar than any organic solvent.
Q. Does a higher Rf value mean more polar?
In general, the adsorptivity of compounds increases with increased polarity (i.e. the more polar the compound then the stronger it binds to the adsorbent). Non-polar compounds move up the plate most rapidly (higher Rf value), whereas polar substances travel up the TLC plate slowly or not at all (lower Rf value).