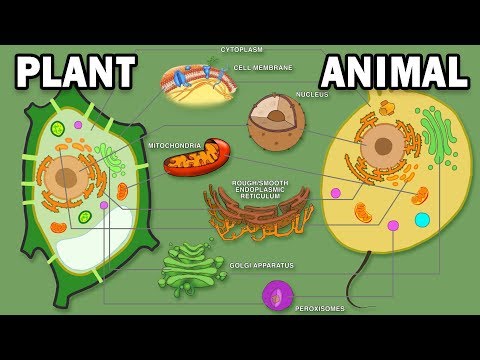
All cells have structural and functional similarities. Structures shared by all cells include a cell membrane, an aqueous cytosol, ribosomes, and genetic material (DNA). All cells are composed of the same four types of organic molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Q. What is an organism with a nuclear membrane and organelles surrounded by membranes?
An organism with a nuclear membrane and organelles surrounded by membranes = eukaryote 10. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane, contains the cells DNA, and acts as the control center.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is an organism with a nuclear membrane and organelles surrounded by membranes?
- Q. What do the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane have in common?
- Q. What is a membrane that surrounds and protects the cell?
- Q. What similarities and differences do prokaryotes have with modern day green plants?
- Q. What type of cell has no membrane-bound organelles?
- Q. What organelles are not in a prokaryote?
- Q. Which cell organelles are membrane bound?
- Q. What are examples of organelles with membranes?
- Q. What are the membrane bound structures in a cell called?
Q. What do the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane have in common?
Similarities Between Cell Membrane and Nuclear Membrane They are made up of lipid bilayers. Furthermore, their main function is to enclose different structures of the cell regulating the passage of molecules through the membrane. Also, they act as semi-permeable membranes.
Q. What is a membrane that surrounds and protects the cell?
The Plasma Membrane—A Cell’s Protective Coat. The outer lining of a eukaryotic cell is called the plasma membrane. This membrane serves to separate and protect a cell from its surrounding environment and is made mostly from a double layer of proteins and lipids, fat-like molecules.
Q. What similarities and differences do prokaryotes have with modern day green plants?
Prokaryotes are similar to green plants because, like plants, prokaryotes perform basic life functions, including reproduction, digestion, and respiration. As far as differences, prokaryotes have one cell, while green plants are multicellular. Plants are also eukaryotes—they have a nucleus.
Q. What type of cell has no membrane-bound organelles?
Prokaryotic cells
Q. What organelles are not in a prokaryote?
The organism is likely a prokaryotic organism, since it lacks a nuclear membrane and mitochondria. Prokaryotes lack all membrane-bound organelles, including nuclei, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplasts, and lysosomes. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes contain ribosomes.
Q. Which cell organelles are membrane bound?
Examples of membrane-bound organelles are nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, plastids, lysosomes and vacuoles.
Q. What are examples of organelles with membranes?
Membranous organelles
- Endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membranes responsible for the production of proteins, metabolism and transportation of lipids, and detoxification of poisons.
- Golgi apparatus.
- Mitochondria.
- Peroxisomes.
- Lysosomes.
- Transport vesicles.
Q. What are the membrane bound structures in a cell called?
An organelle (think of it as a cell’s internal organ) is a membrane bound structure found within a cell.