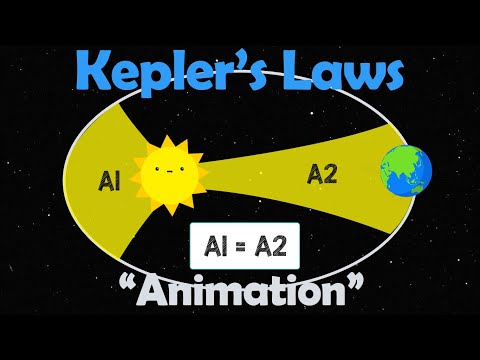
There are actually three, Kepler’s laws that is, of planetary motion: 1) every planet’s orbit is an ellipse with the Sun at a focus; 2) a line joining the Sun and a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times; and 3) the square of a planet’s orbital period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its …
Q. What did Kepler discover?
Johannes Kepler, (born December 27, 1571, Weil der Stadt, Württemberg [Germany]—died November 15, 1630, Regensburg), German astronomer who discovered three major laws of planetary motion, conventionally designated as follows: (1) the planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus; (2) the time necessary to …
Table of Contents
- Q. What did Kepler discover?
- Q. What did Kepler discover about the orbits of the planets?
- Q. How did Kepler discover the elliptical orbit?
- Q. What do Kepler’s three laws imply about Orbit shape speed of one complete orbit period and orbital size semi major axis <UNK>?
- Q. What is Kepler’s third law formula?
- Q. What is K in Kepler’s third law?
- Q. Why does Kepler’s third law work?
- Q. What is Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law?
- Q. What is G in Kepler’s law?
- Q. What determines the shape of orbit?
- Q. What does P 2 a 3 mean?
- Q. Which planet is closest to the sun?
- Q. What is the closest point to the sun in a planets orbit called?
- Q. Do planets move faster when they are closer to the sun?
- Q. What month is the planet moving the fastest?
- Q. Which planet is moving the fastest?
- Q. What color are all the planets?
- Q. Who named Sun?
- Q. What planet is not named after a god?
- Q. Who named all the planets?
- Q. How many planet are not named after a god?
- Q. How many planets in our solar system are not named after a god goddess?
Q. What did Kepler discover about the orbits of the planets?
Through Brahe’s astronomical measurements and Kepler’s own drawings of the geometrical relationship between the Sun and Mars in various parts of the planet’s orbit, Kepler discovered that planets moved faster when they were closer to the Sun.
Q. How did Kepler discover the elliptical orbit?
He inherited Tycho’s post as Imperial Mathematician when Tycho died in 1601. Using the precise data that Tycho had collected, Kepler discovered that the orbit of Mars was an ellipse. In 1609 he published Astronomia Nova, delineating his discoveries, which are now called Kepler’s first two laws of planetary motion.
Q. What do Kepler’s three laws imply about Orbit shape speed of one complete orbit period and orbital size semi major axis <UNK>?
Kepler’s Third Law: the squares of the orbital periods of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of the semi major axes of their orbits. Kepler’s Third Law implies that the period for a planet to orbit the Sun increases rapidly with the radius of its orbit.
Q. What is Kepler’s third law formula?
If the size of the orbit (a) is expressed in astronomical units (1 AU equals the average distance between the Earth and Sun) and the period (P) is measured in years, then Kepler’s Third Law says P2 = a3.
Q. What is K in Kepler’s third law?
As a consequence of law of gravitation and Kepler’s third law, k is directly proportional to the square root of the standard gravitational parameter of the Sun, and its value in radians per day follows by setting Earth’s semi-major axis (the astronomical unit, au) to unity, k:(rad/d) = (G M ☉)0.5·au−1.5.
Q. Why does Kepler’s third law work?
“The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit” That’s Kepler’s third law. In other words, if you square the ‘year’ of each planet, and divide it by the cube of its distance to the Sun, you get the same number, for all planets.
Q. What is Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law?
Newton developed a more general form of what was called Kepler’s Third Law that could apply to any two objects orbiting a common center of mass. This is called Newton’s Version of Kepler’s Third Law: M1 + M2 = A3 / P2. Special units must be used to make this equation work.
Q. What is G in Kepler’s law?
The Newtonian constant, G, is defined in terms of the force between two two masses separated by some fixed distance. In order to measure k, all you need to do is count days; in order to measure G, you need to know very precisely the masses, separation, and forces between test objects in a laboratory.
Q. What determines the shape of orbit?
Orbital Speed determines the orbit shape: Circular Speed. Escape Speed.
Q. What does P 2 a 3 mean?
There is a simplified version of this law: P2 = a3 where: The object must be orbiting the Sun. P = period of the orbit in years. a = average distance of the object from the Sun in AU.
Q. Which planet is closest to the sun?
Mercury
Q. What is the closest point to the sun in a planets orbit called?
perihelion
Q. Do planets move faster when they are closer to the sun?
Therefore the planet moves faster when it is nearer the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun. A planet moves with constantly changing speed as it moves about its orbit. The fastest a planet moves is at perihelion (closest) and the slowest is at aphelion (farthest).
Q. What month is the planet moving the fastest?
January
Q. Which planet is moving the fastest?
Q. What color are all the planets?
Colour therapy is also the foundation for Vedic gem therapy and basic colours of the planets are: SUN—Red (transparent), MOON—White (opaque), MARS—Red (opaque), MERCURY—Green, JUPITER- Yellow, VENUS—White (transparent), SATURN—Blue.
Q. Who named Sun?
The word sun comes from the Old English word sunne, which itself comes from the older Proto-Germanic language’s word sunnōn. In ancient times the Sun was widely seen as a god, and the name for Sun was the name of that god. Ancient Greeks called the Sun Helios, and this word is still used to describe the Sun today.
Q. What planet is not named after a god?
Earth
Q. Who named all the planets?
All of the planets, except for Earth, were named after Greek and Roman gods and godesses. Jupiter, Saturn, Mars, Venus and Mercury were given their names thousands of years ago. The other planets were not discovered until much later, after telescopes were invented.
Q. How many planet are not named after a god?
According to Universe Today, Earth is the only planet not named after a Roman god or goddess, but it is associated with the goddess Terra Mater (Gaea to the Greeks). In mythology, she was the first goddess on Earth and the mother of Uranus.
Q. How many planets in our solar system are not named after a god goddess?
The Babylonians called the planet Ishtar after their goddess of womanhood and love. Earth is the only planet not named after a Roman god or goddess, but it is associated with the goddess Terra Mater (Gaea to the Greeks). In mythology, she was the first goddess on Earth and the mother of Uranus.