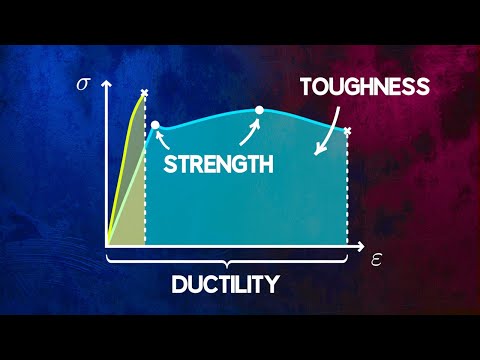
Ductility allows structures to bend and deform to some extent without rupturing. High ductility is critical in applications such as metal cables and structural beams. Gold, silver and platinum are ductile metals.
Q. What is some examples of ductility?
Ductility is the physical property of a material associated with the ability to be hammered thin or stretched into wire without breaking. A ductile substance can be drawn into a wire. Examples: Most metals are good examples of ductile materials, including gold, silver, copper, erbium, terbium, and samarium.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is some examples of ductility?
- Q. What is ductility Why is it important?
- Q. How do you say ductility?
- Q. What does malleable mean?
- Q. How do you spell malleable?
- Q. Can a person be malleable?
- Q. What causes malleability?
- Q. What is malleability used for?
- Q. What is Silver’s original name?
- Q. How is malleability tested?
- Q. How is ductility tested?
- Q. How do you test for toughness?
- Q. What is creep behavior?
Q. What is ductility Why is it important?
Ductility is especially important in metalworking, as materials that crack, break or shatter under stress cannot be manipulated using metal-forming processes such as hammering, rolling, drawing or extruding.
Q. How do you say ductility?
Here are 4 tips that should help you perfect your pronunciation of ‘ductility’:
- Break ‘ductility’ down into sounds: [DUK] + [TIL] + [UH] + [TEE] – say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them.
- Record yourself saying ‘ductility’ in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen.
Q. What does malleable mean?
1 : capable of being extended or shaped by beating with a hammer or by the pressure of rollers. 2a : capable of being altered or controlled by outside forces or influences.
Q. How do you spell malleable?
noun. the state of being malleable, or capable of being shaped, as by hammering or pressing: the extreme malleability of gold. adaptability: the malleability of an infant’s brain.
Q. Can a person be malleable?
If you say that someone is malleable, you mean that they are easily influenced or controlled by other people. She was young enough to be malleable. A substance that is malleable is soft and can easily be made into different shapes. Silver is the most malleable of all metals.
Q. What causes malleability?
Malleability in metals occurs because of the metallic bonds that keep the atoms in place. Metallic bonds, characterized by a ‘sea’ of electrons that easily move from atom to another, allow the metal atoms to slide past each other if a force is applied.
Q. What is malleability used for?
Industrial containers , huge sheets, many parts in machines are made because of malleability of strong metals. Say even the railway wagons are made of sheets because of malleability of the metals and alloys. 4. Malleability also allows for repairs of some metallic objects if they are deformed.
Q. What is Silver’s original name?
Our name for the element is derived from the Anglo-Saxon for silver, ‘seolfor,’ which itself comes from ancient Germanic ‘silabar. ‘ Silver’s chemical symbol, Ag, is an abbreviation of the Latin word for silver, ‘argentum. ‘ The Latin word originates from argunas, a Sanskrit word meaning shining.
Q. How is malleability tested?
malleability and ductility tests punch and force from a hammer. # The smaller the indent, the harder the material. piece is bent to an angle of 90 degrees: cracks on the outside indicate a lack of ductility cracks on the inside indicate a lack of malleability.
Q. How is ductility tested?
Ductility involves determining the extent by which a material can withstand plastic deformation without rupture. A bend test for ductility provides a simple way to evaluate the quality of materials by their ability to resist cracking or other surface irregularities during one continuous bend.
Q. How do you test for toughness?
Therefore, one way to measure toughness is by calculating the area under the stress strain curve from a tensile test. This value is simply called “material toughness” and it has units of energy per volume. Material toughness equates to a slow absorption of energy by the material.
Q. What is creep behavior?
In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material.