A dihedral angle of a protein is the internal angle of polypeptide backbone at which two adjacent planes meet. The conformation of the backbone can be described by two dihedral angles per residue, because the backbone residing between two juxtaposing Cα atoms are all in a single plane.
Q. What is meant by torsional angle?
: the angle through which a radial section of a body (as a wire or a shaft) deflects from its normal position when the body is subjected to torque.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is meant by torsional angle?
- Q. What are phi and psi angles in proteins?
- Q. What is the omega angle in protein?
- Q. What is torsion angle in DNA?
- Q. What is the role of dihedral angle in proteins?
- Q. What is Phi angle?
- Q. How do you read Psi and Phi angles?
- Q. How do you find torsion angle?
- Q. What is torsion angle in chemistry?
- Q. How many nucleotides are in a turn of Helix?
- Q. How are torsion angles related to the structure of a protein?
- Q. What are the torsion angles of peptide bonds?
- Q. Is the dihedral angle the same as the torsion angle?
- Q. How does the Ramachandran plot show torsion angles?
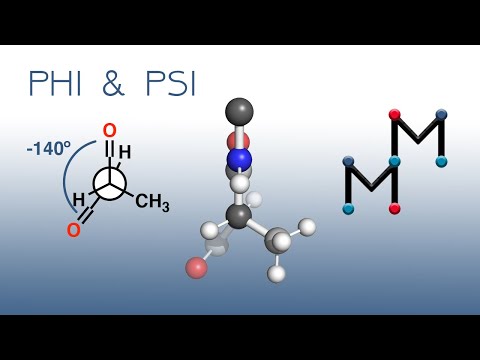
Q. What are phi and psi angles in proteins?
Amino acid residues in the beta-conformation have negative phi angles and the psi angles are positive. Typical values are phi = -140 degrees and psi = 130 degrees. In contrast, alpha-helical residues have both phi and psi negative.
Q. What is the omega angle in protein?
The omega (ω) angle in peptide is the torsion angle measured over the peptide bond, the chemical bond that connects two amino acids. Because this bond has a little bit of a double-bonded character the (ω)-angle is almost 180 degrees.
Q. What is torsion angle in DNA?
Except for pseudouridine, a nucleoside in DNA/RNA contains an N-glycosidic bond that connects the base to the sugar. The chi (χ) torsion angle, which characterizes the relative base/sugar orientation, is defined by O4′-C1′-N1-C2 for pyrimidines (C, T and U), and O4′-C1′-N9-C4 for purines (A and G).
Q. What is the role of dihedral angle in proteins?
Dihedral angles are of considerable importance in protein structure prediction as they define the backbone of a protein, which together with side chains define the entire protein conformation.
Q. What is Phi angle?
The angle between two bonds The backbone of a protein has three different torsion angles. The phi-angle (φ) – around the N-Cα bond. The psi-angle (ψ) – around the Cα-C bond. The omega-angle (ω) – around the peptide bond between C and N.
Q. How do you read Psi and Phi angles?
In sequence order, phi (φ) is the C(i-1),N(i),Ca(i),C(i) torsion angle and psi (ψ) is the N(i),Ca(i),C(i),N(i+1) torsion angle.
Q. How do you find torsion angle?
Now the torsion angle is defined as the angle between the two vectors, b_a_orth and c_d_orth, and can be easily calculated by their dot product. The sign of the torsion angle is determined by the relative orientation of the cross product of the same two vectors with reference to the middle vector b→c.
Q. What is torsion angle in chemistry?
A torsion angle ϕ is defined by four consecutive covalently bonded atoms. It is the angle by which atom 4 has to rotate counterclockwise around the axis defined by the rotatable bond (atoms 2 and 3) to be in plane with atoms 1, 2, and 3.
Q. How many nucleotides are in a turn of Helix?
Z-form DNA
| B-Form | A-Form | |
|---|---|---|
| helix sense | Right Handed | Right Handed |
| base pairs per turn | 10 | 11 |
| vertical rise per bp | 3.4 Å | 2.56 Å |
| rotation per bp | +36° | +33° |
Q. How are torsion angles related to the structure of a protein?
The Ramachandran plot provides a way to view the distribution of torsion angles in a protein structure and shows that the torsion angles corresponding to the two major secondary structure elements (α-helices and β-sheets) are clearly clustered within separate regions. The images below correspond to two different structures of the same protein.
Q. What are the torsion angles of peptide bonds?
The figure below shows the three main chain torsion angles of a polypeptide. These are phi, psi and omega. The planarity of the peptide bond restricts omega to 180 degrees in very nearly all of the main chain peptide bonds.
Q. Is the dihedral angle the same as the torsion angle?
Since the torsion angle depends only on the vectors a, b, c also write ˚= ˝(a;b;c): In this case the torsion angle is also called the dihedral angle. The angle is usually measured in degrees and chosen in the interval ( 180;180]. The dihedral angle can be thought of as the angle between two planes.
Q. How does the Ramachandran plot show torsion angles?
The Ramachandran plot shows the distribution of the torsion angles of a protein within certain regions. The horizontal axis on the plot shows φ values, while the vertical shows ψ values.