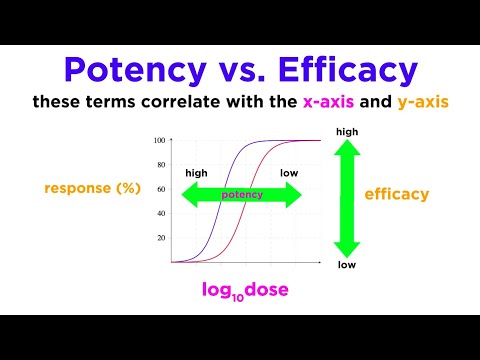
Pharmacodynamics is affected by receptor binding and sensitivity, postreceptor effects, and chemical interactions. Both pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics explain the drug’s effects, which is the relationship between the dose and response. The pharmacologic response depends on the drug binding to its target.
Q. What is the study of pharmacodynamics?
Pharmacodynamics (sometimes described as what a drug does to the body) is the study of the biochemical, physiologic, and molecular effects of drugs on the body and involves receptor binding (including receptor sensitivity), postreceptor effects, and chemical interactions.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the study of pharmacodynamics?
- Q. Why is studying pharmacodynamics important?
- Q. What is an example of pharmacodynamics?
- Q. What are the principles of pharmacodynamics?
- Q. What is pharmacodynamic effect?
- Q. What is primary pharmacodynamics?
- Q. What is the difference between primary and secondary pharmacodynamic studies?
- Q. What is primary and secondary pharmacodynamics?
- Q. What is the difference between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
- Q. What is PK study?
- Q. What is the pharmacodynamics of penicillin?
- Q. What is pharmacodynamics in simple language?
- Q. What is a post antibiotic effect?
- Q. Is Penicillin time-dependent?
- Q. Which antibiotics are time-dependent?
- Q. Which antibiotics have a post antibiotic effect?
- Q. How does amoxicillin work in the body?
- Q. What infections does amoxicillin cure?
- Q. What is the side effects of amoxicillin?
- Q. Do antibiotics make you tired and weak?
- Q. Can amoxicillin make you sleepy?
- Q. Do antibiotics weaken your immune system?
- Q. How long do antibiotics stay in your system?
- Q. Do antibiotics make you lose weight?
Q. Why is studying pharmacodynamics important?
Pharmacology and pharmacodynamics studies are of great importance in determining a drug’s effect during drug discovery and development. Creative Biolabs provides pharmacology and pharmacodynamics analyses and builds various animal models to describe the time course of effect in response to a drug dose.
Q. What is an example of pharmacodynamics?
Drug interactions occur on pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic levels. Examples of pharmacodynamic interactions are simultaneous administration of a NSAID and phenprocoumon (additive interaction), or of aspirin and ibuprofen (antagonistic interaction).
Q. What are the principles of pharmacodynamics?
Pharmacodynamic mechanisms regulate the effects of drugs on the human body. As noted earlier, drug-receptor binding results in multiple, complex chemical interactions. The site on the receptor at which a drug binds is called its binding site.
Q. What is pharmacodynamic effect?
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection).
Q. What is primary pharmacodynamics?
Primary pharmacodynamics can be defined as studies on the mode of action and/or effects of a substance in relation to its desired therapeutic target.
Q. What is the difference between primary and secondary pharmacodynamic studies?
Primary pharmacodynamic studies do not need to be conducted in compliance with GLP. Generally, secondary pharmacodynamic studies do not need to be conducted in compliance with GLP.
Q. What is primary and secondary pharmacodynamics?
Primary pharmacodynamics – primary action in target system. B. Secondary pharmacodynamics – resultant action in target systems, not. related to the intended target.
Q. What is the difference between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics?
In simple words, pharmacokinetics is ‘what the body does to the drug’. Pharmacodynamics describes the intensity of a drug effect in relation to its concentration in a body fluid, usually at the site of drug action.
Q. What is PK study?
A pharmacokinetic (PK) study of a new drug involves taking several blood samples over a period of time from study participants to determine how the body handles the substance. These studies provide critical information about new drugs.
Q. What is the pharmacodynamics of penicillin?
When large amounts of penicillin are available, the enzyme is completely blocked. When small amounts of penicillin are available, the enzyme resumes normal function. Thus the bacterial-killing activity of penicillin changes as drug levels in the body change. This is considered the “pharmacodynamics” of penicillin.
Q. What is pharmacodynamics in simple language?
Pharmacodynamics is the study of a drug’s molecular, biochemical, and physiologic effects or actions. It comes from the Greek words “pharmakon” meaning “drug” and “dynamikos” meaning “power.”
Q. What is a post antibiotic effect?
The term postantibiotic effect (PAE) refers to a period of time after complete removal of an antibiotic during which there is no growth of the target organism. The PAE appears to be a feature of most antimicrobial agents and has been documented with a variety of common bacterial pathogens.
Q. Is Penicillin time-dependent?
Time-Dependent Killing: For instance, certain antibiotics, like beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams), clindamycin, macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin), oxazolidinones (linezolid), can be effective because of the extensive amount of time the antibiotic binds to the microorganism.
Q. Which antibiotics are time-dependent?
Tables
| Antibiotic Class | Pharmacodynamic Profile | Pharmacodynamic Parameter to Optimize |
|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Time-dependent | Time>MIC |
| Cephalosporins | Time-dependent | Time>MIC |
| Carbapenems | Time-dependent | Time>MIC |
| Vancomycin | Time-dependent | AUC:MIC |
Q. Which antibiotics have a post antibiotic effect?
It has been suggested that an alteration of DNA function is possibly responsible for post antibiotic effect following the observation that most inhibitors of protein and nucleic acid synthesis (aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines, clindamycin, certain newer macrolides/ketolides, and rifampicin and …
Q. How does amoxicillin work in the body?
Amoxicillin is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. This medication is a penicillin-type antibiotic. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections.
Q. What infections does amoxicillin cure?
About amoxicillin Amoxicillin is an antibiotic. It’s used to treat bacterial infections, such as chest infections (including pneumonia), dental abscesses and urinary tract infections (UTIs). It’s used in children, often to treat ear infections and chest infections. The medicine is only available on prescription.
Q. What is the side effects of amoxicillin?
Side Effects
- Abdominal or stomach cramps or tenderness.
- back, leg, or stomach pains.
- black, tarry stools.
- bloating.
- blood in the urine.
- bloody nose.
- diarrhea, watery and severe, which may also be bloody.
- feeling of discomfort.
Q. Do antibiotics make you tired and weak?
If you’re taking prescription antibiotics, you may feel tired and fatigued. This may be a symptom of the infection being treated by the antibiotics, or it may be a serious, but rare, side effect of the antibiotic.
Q. Can amoxicillin make you sleepy?
When taking amoxicillin to combat an infection, it’s normal to feel tired. However, if you’re excessively tired to the point of feeling weak, faint, or struggling to stay awake, get medical attention.
Q. Do antibiotics weaken your immune system?
Will antibiotics weaken my immune system? Very rarely, antibiotic treatment will cause a drop in the blood count, including the numbers of white cells that fight infection. This corrects itself when the treatment is stopped.
Q. How long do antibiotics stay in your system?
Each antibiotic may stay in the body for different lengths of time, but common antibiotics such as amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin stay in your system for about 24 hours after taking the last dose. It might take longer for people with impaired kidney function to eliminate the drug from the body.
Q. Do antibiotics make you lose weight?
Antibiotics can cause weight loss by impairing gut microbiota in mice and the potent benefits of lactobacilli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.