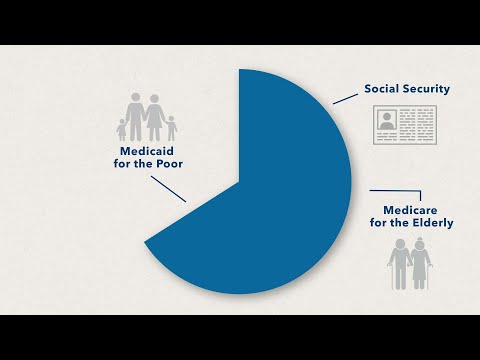
The United States federal budget consists of mandatory expenditures (which includes Medicare and Social Security), discretionary spending for defense, Cabinet departments (e.g., Justice Department) and agencies (e.g., Securities & Exchange Commission), and interest payments on debt.
Q. What is the difference between mandatory spending and discretionary spending quizlet?
What is the difference between mandatory spending and discretionary spending? Mandatory spending is spending that is required by current law and discretionary spending is spending that must be authorized by the government each year.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the difference between mandatory spending and discretionary spending quizlet?
- Q. What is the difference between discretionary and non discretionary spending?
- Q. What are 2 examples of discretionary spending?
- Q. What does it mean for spending to be mandatory?
- Q. Can mandatory spending be changed?
- Q. Who spends the most on military?
- Q. Where does most of the US budget go?
- Q. What is the biggest expense of the US government?
- Q. What percentage of taxes go to welfare?
- Q. What are the three largest categories of federal government spending?
- Q. Who will present Budget 2020?
- Q. Is New Budget 2020 good?
- Q. What are the 70 exemptions removed in Budget 2020?
- Q. What are the 70 exemptions?
- Q. Which deduction is still allowed for 2020?
- Q. Which regime is better for income tax?
- Q. Which is best tax Old or new?
- Q. Can we change income tax regime every year?
- Q. What deductions are not allowed in new tax regime?
- Q. Is HRA applicable for new tax regime?
- Q. What deductions are allowed for income tax?
- Q. Can I change from new tax regime to old?
- Q. Is PF exempted in new tax regime?
- Q. Are you filing return of income under seventh?
- Q. Do you want to claim the benefit u/s 115H?
Q. What is the difference between discretionary and non discretionary spending?
Expenses are divided into several categories, namely non-discretionary and discretionary. While non-discretionary expenses are considered mandatory—housing, taxes, debt, groceries—discretionary expenses are any costs incurred above and beyond what is deemed necessary.
Q. What are 2 examples of discretionary spending?
Some examples of areas funded by discretionary spending are national defense, foreign aid, education and transportation.
Q. What does it mean for spending to be mandatory?
Mandatory—or direct—spending includes spending for entitlement programs and certain other payments to people, businesses, and state and local governments. Mandatory spending is generally governed by statutory criteria; it is not normally set by annual appropriation acts.
Q. Can mandatory spending be changed?
For example, Congress amended the Social Security Act to create Medicare. For this reason, mandatory programs are outside the annual budget process that governs discretionary spending. Since it is so difficult to change mandatory spending, it is not part of the discretionary fiscal policy.
Q. Who spends the most on military?
USA
Q. Where does most of the US budget go?
More than half of FY 2019 discretionary spending went for national defense, and most of the rest went for domestic programs, including transportation, education and training, veterans’ benefits, income security, and health care (figure 4).
Q. What is the biggest expense of the US government?
Social Security will be the biggest expense, budgeted at $1.151 trillion. It’s followed by Medicare at $722 billion and Medicaid at $448 billion. Social Security costs are currently 100% covered by payroll taxes and interest on investments.
Q. What percentage of taxes go to welfare?
Safety net programs: About 8 percent of the federal budget in 2019, or $361 billion, supported programs that provide aid (other than health insurance or Social Security benefits) to individuals and families facing hardship.
Q. What are the three largest categories of federal government spending?
Federal spending can be divided into three general categories: mandatory, discretionary, and interest on the debt. Mandatory spending has numerous parts, but the largest ones are major healthcare programs (Medicare and Medicaid) and Social Security.
Q. Who will present Budget 2020?
Nirmala Sitharaman
Q. Is New Budget 2020 good?
* Offering an optional lower rate of income tax to individuals, Sitharaman in her Budget for 2020-21 proposed new tax slabs of 15 per cent and 25 per cent in addition to the existing 10 per cent, 20 per cent and 30 per cent. Those individuals earning between Rs 2.5 lakh and Rs 5 lakh will pay 5 per cent tax.
Q. What are the 70 exemptions removed in Budget 2020?
What’s out: Here are a few of the 70 exemptions and deductions you won’t see in the new regime- Section 80C investments, house rent allowance, home loan interest, leave travel allowance, medical insurance premium, standard deduction, savings account interest, education loan interest.
Q. What are the 70 exemptions?
What’s out Some of the 70 exemptions and deductions you won’t get in new regime.
- Section 80C investments.
- House rent allowance.
- Housing loan interest.
- Leave travel allowance.
- Medical insurance premium.
- Standard deduction.
- Savings bank interest.
- Education loan interest.
Q. Which deduction is still allowed for 2020?
(xii) Deduction under section 35AD or section 35CCC; (xiii) Deduction from family pension under section 57(iia); (xiv) Any deduction under chapter VIA (like section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD, 80D, 80DD, 80DDB, 80E, 80EE, 80EEA, 80EEB, 80G, 80GG, 80GGA, 80GGC, 80IA, 80-IAB, 80-IAC, 80-IB, 80-IBA, etc).
Q. Which regime is better for income tax?
New taxation regime is better for employees with less salary and less investments resulting in lesser deductions and exemptions.
Q. Which is best tax Old or new?
Taxpayers with annual income between RS. 5 lakhs to Rs. 10 lakhs are taxed at 20%, under the old regime….Old vs New: A Comparison For Different Slabs.
| OLD RATES (with exemptions) | ANNUAL INCOME | NEW RATE (without exemptions) |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | Rs. 7.5 – 10 lakh | 15% |
| 30% | Rs. 10-12.5 lakh | 20% |
| Rs. 12.5-15 lakh | 25% | |
| Rs. 15 and above | 30% |
Q. Can we change income tax regime every year?
Effectively, you can switch between new and old tax regime at the time of filing ITR. CBDT also clarifies that even if one opts for New Tax Regime and the same intimation is made to employer or Deductor, it shall be only for the purposes of TDS during the previous year and cannot be modified during that year.
Q. What deductions are not allowed in new tax regime?
3. Exemptions and deductions not claimable under the new tax regime
- The standard deduction, professional tax and entertainment allowance on salaries.
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
- House Rent Allowance (HRA)
- Minor child income allowance.
- Helper allowance.
- Children education allowance.
- Other special allowances [Section10(14)]
Q. Is HRA applicable for new tax regime?
HRA is a major component of an employees’ salary as it varies between 40-50% of basic salary. So the tax benefit available on HRA is a big relief for salaried individuals. If you opt for the new tax regime, that aims to tax your income at lower slab rates, you will have to forego the HRA benefit.
Q. What deductions are allowed for income tax?
- Exemption of House Rent Allowance. A salaried individual having a rented accommodation can get the benefit of HRA (House Rent Allowance).
- Standard Deduction.
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
- Mobile reimbursement.
- Books and Periodicals.
- Food coupons.
- Section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD(1)
- Medical Insurance Deduction (Section 80D)
Q. Can I change from new tax regime to old?
As per the laws, the employees have to choose between the old and the new tax regime and inform their employers about their choices, however, if one is not certain with the choice then he/she can certainly change his/her decision at the time of ITR filing.
Q. Is PF exempted in new tax regime?
Contribution By Employer Towards’ Employees NPS/EPF Account For the FY 2020-21, the employer’s contributions towards superannuation, EPF, NPS is available for tax exemption up to a maximum limit of Rs. 7.5 lakh. Currently, the employer’s contribution towards EPF remains 12% of the employee’s basic salary.
Q. Are you filing return of income under seventh?
2) Act, 2019 has inserted a new seventh proviso to section 139(1) of the Income Tax Act, 1961 (‘the IT Act’) w.e.f. to provide for mandatory filing of ITR for those people who have certain high-value transactions even though that person is otherwise not required to file a return of income due to the fact …
Q. Do you want to claim the benefit u/s 115H?
Section 115H – Benefit under Chapter to be available in certain cases even after the assessee becomes resident – Income-tax Act, 1961. ….. Where a person, who is a non-resident Indian in any previous year, becomes assessable as resident in India in respect of the total income of any su …..