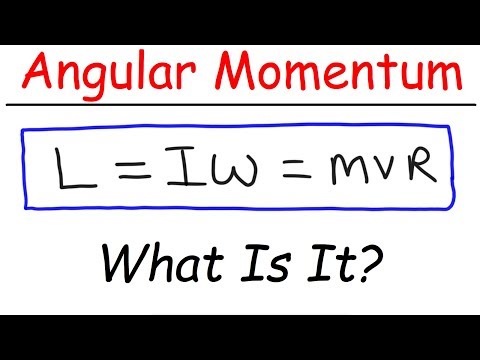
Angular momentum of an object with linear momentum is proportional to mass, linear velocity, and perpendicular radius from an axis to the line of the object’s motion.
Q. What is the kinetic energy of the disk?
The kinetic energy of the disk therefore is KEtot = (3/4)mr2ω2. The ratio of the translational to the rotational kinetic energy is Etrans/Erot = mr2/I.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the kinetic energy of the disk?
- Q. How much is the angular momentum of Earth about its own axis?
- Q. Why does angular momentum increase with radius?
- Q. Is angular momentum conserved in non uniform circular motion?
- Q. Is kinetic energy conserved in circular motion?
- Q. How does rotational inertia affect kinetic energy?
- Q. Is kinetic energy conserved with angular momentum?
- Q. Why kinetic energy is half potential energy?
- Q. What are the similarities between kinetic and potential energy?
- Q. What does the 1 2 mean in kinetic energy?
Q. How much is the angular momentum of Earth about its own axis?
L=7×1033kg/m2/sec.
Q. Why does angular momentum increase with radius?
The angular momentum of an object moving in a circle with radius ‘r’ is the product of the mass, velocity or speed of rotation, and the radius of the circle. For example, if the mass decreases, the velocity or radius must increase to compensate for this in order to keep the value of angular momentum the same.
Q. Is angular momentum conserved in non uniform circular motion?
The uniform circular motion is characterized by constant speed. Hence, speed is conserved. The particle has constant angular velocity (ω) and constant moment of inertia (I) about the axis of rotation. Hence, angular momentum (Iω) is conserved.
Q. Is kinetic energy conserved in circular motion?
Just as in translational motion (where kinetic energy equals 1/2mv2 where m is mass and v is velocity ), energy is conserved in rotational motion. However, the energy is never destroyed; it merely changes form from rotation of the grindstone to heat when friction is applied.
Q. How does rotational inertia affect kinetic energy?
Rotational kinetic energy is directly proportional to the rotational inertia and the square of the magnitude of the angular velocity.
Q. Is kinetic energy conserved with angular momentum?
Energy is conserved in rotational motion just as in translational motion. The rotational kinetic energy is the kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object and is part of its total kinetic energy. …
Q. Why kinetic energy is half potential energy?
Negative kinetic energy equals half the potential energy (−K = ½U). Potential energy equals twice the total energy (U = 2E). Twice the kinetic energy plus the potential energy equals zero (2K + U = 0).
Q. What are the similarities between kinetic and potential energy?
Kinetic and potential energy are both typically ascribed as forms of mechanical energy and can be interchangeably converted. Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy and vice versa, but the change is always accompanied by the dissipation of some energy as heat.
Q. What does the 1 2 mean in kinetic energy?
KINETIC ENERGY-K.E = 1/2 mv2. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity .[