Re: Why Ag+ is a Lewis acid not base? Ag+ is an electron pair acceptor (Lewis acid) because it is positively charged. As I discussed in class electrons are electrostatically attracted to the positive charge.
Q. Is AgOH a salt base or acid?
Cards
Table of Contents
| Term List the common strong acids. | Definition HCL (hydrochloric acid), HBr (hydrobromic acid), HI (Hydroiodic “), HNO3 (Nitric acid), H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid), HClO4 (perchloric acid) |
|---|---|
| Term Which of the following are strong bases? LiOH, AgOH, Pb(OH)2, NaCl, KOH, CaOH, NaOH | Definition LiOH, KOH, NaOH |
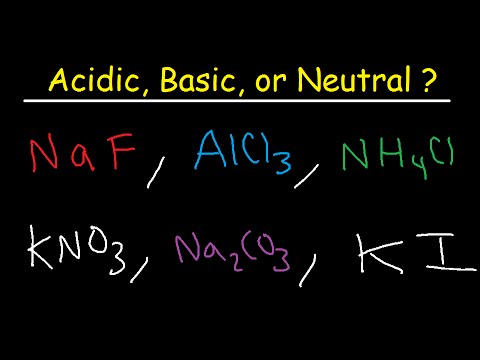
Q. Is Al3+ acidic or basic?
Compounds containing cations other than H+ are acids! Example: Al3+ (aq) = ≈ pH 3! A BASE DONATES unbonded ELECTRON PAIR/S.
Q. Why is Al3+ not a Bronsted acid?
Compounds containing cations other than H+ are acids! Example: Al3+ (aq) = ≈ pH 3! A BASE DONATES unbonded ELECTRON PAIR/S. HCl, H2SO4 are Bronsted acids because they can donate protons, but they cannot accept a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond, therefore, they are not Lewis acids.
Q. Is Cu2+ A Lewis base?
Cu2+ (aq) reacts with ammonia to form the complex ion [Cu(NH)3)4]2+. Ammonia acts as the Lewis base in this reaction by donating its lone pair of electrons, whilst Cu2+ (which is an electron deficient, electrophile) accepts the lone pair of electrons from the ammonia, making it a Lewis acid.
Q. Is Cu 2 a Lewis acid or base?
Cu^2 + ion can act as Lewis acid and NH3 is a Lewis base.
Q. Is CU NH3 4 2+ a precipitate?
The addition of ammonia to a Cu2+ solution causes the formation of the dark blue complex ion [Cu(NH3)4]2+. When potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) is added to a Cu2+ solution, a reddish precipitate of copper(II) hexacyanoferrate(II) is formed.
Q. Is CU NH3 4 soluble in water?
Tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate is the salt with the formula [Cu(NH3)4]SO4·H2O. This dark blue to purple solid is a salt of the metal complex [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)]2+….Tetraamminecopper(II) sulfate.
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Solubility in water | 18.5 g/100 g (21.5 °C) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Q. Why is CU NH3 2 Colourless?
A compound which have unpaired electron can impart colour due to d-d transition. [Cu(NH3)4]2+ has unpaired electron. Hence, [Cu(NH3)4]2+ ion is coloured whereas [Cu(CN)4]3–does not have unpaired electron. it is a colourless compound.
Q. What Colour is co NH3 6 2+?
Cards
| Term [Cu(H20)6]2+ | Definition Blue Solution |
|---|---|
| Term [Co(NH3)6]2+ | Definition Straw-coloured Solution |
| Term [Co(NH3)6]3+ | Definition Yellow Solution (Appears dark brown due to other compounds) |
| Term [CoCl4]2- | Definition Blue Solution |
| Term [Co(H2O)4(OH)2] | Definition Green-Blue Precipitate |