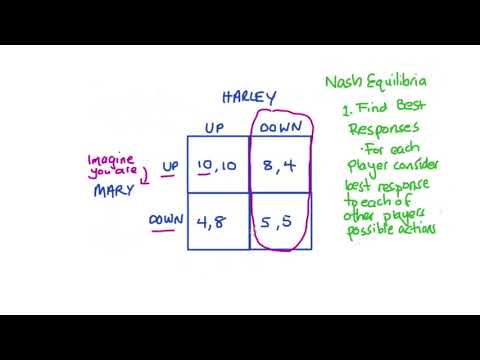
Answer: A player’s best response is not the same as his dominant strategy. A best response is simply one player’s optimal choice, taking the other player’s action as given. In other words, a best response gives a player a payoff that is at least as large as the payoff from any other strategy she has available.
Q. What is dominant and dominated strategy?
A strategy is dominant if it leads to better outcomes than alternative strategies, and dominated if it leads to worse outcomes than alternative strategies.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is dominant and dominated strategy?
- Q. Is there always a dominant strategy in game theory?
- Q. What is the best response strategy?
- Q. What is the row players dominant strategy?
- Q. What is the difference between pure and mixed strategy?
- Q. How many pure strategies are available to each player?
- Q. How many strategies does Player 2 have?
- Q. What is a proper Subgame?
- Q. How do you calculate Subgame?
- Q. Is every Nash equilibrium Subgame perfect?
- Q. How do you solve Subgame perfect equilibrium?
- Q. How do you do Nash equilibrium?
- Q. What is a unique subgame perfect equilibrium?
- Q. Can there be two SPNE?
- Q. Is SPNE always ne?
- Q. What is first mover advantage in game theory?
- Q. Who got the first mover advantage?
- Q. Is Netflix a first mover?
- Q. What is the last mover advantage?
Q. Is there always a dominant strategy in game theory?
Dominant strategies are considered as better than other strategies, no matter what other players might do. In game theory, there are two kinds of strategic dominance: It must be noted that any dominant strategy equilibrium is always a Nash equilibrium. However, not all Nash equilibria are dominant strategy equilibria.
Q. What is the best response strategy?
In game theory, the best response is the strategy (or strategies) which produces the most favorable outcome for a player, taking other players’ strategies as given (Fudenberg & Tirole 1991, p. 29; Gibbons 1992, pp. 33–49).
Q. What is the row players dominant strategy?
Here, there is no honor or friendship among thieves, and Row and Column only care about what they themselves will get. This is called a dominant strategyA strategy that is optimal no matter what the other players do., a strategy that is optimal no matter what the other players do.
Q. What is the difference between pure and mixed strategy?
2 Answers. A pure strategy determines all your moves during the game (and should therefore specify your moves for all possible other players’ moves). A mixed strategy is a probability distribution over all possible pure strategies (some of which may get zero weight).
Q. How many pure strategies are available to each player?
4 pure strategies
Q. How many strategies does Player 2 have?
27
Q. What is a proper Subgame?
The part of the game tree consisting of all nodes that can be reached from x is called a subgame. A subgame on a strictly smaller set of nodes is called a proper subgame. A subgame perfect equilibrium is a strategy profile that induces a Nash equilibrium in each subgame.
Q. How do you calculate Subgame?
In order to find the subgame-perfect equilibrium, we must do a backwards induction, starting at the last move of the game, then proceed to the second to last move, and so on.
Q. Is every Nash equilibrium Subgame perfect?
Definition 11.1 A Nash equilibrium is said to be subgame perfect if an only if it is a Nash equilibrium in every subgame of the game. The third subgame is the game itself. Note that, in each subgame, the equilibrium computed via backward induction remains to be an equilibrium of the subgame.
Q. How do you solve Subgame perfect equilibrium?
To solve this game, first find the Nash Equilibria by mutual best response of Subgame 1. Then use backwards induction and plug in (A,X) → (3,4) so that (3,4) become the payoffs for Subgame 2. The dashed line indicates that player 2 does not know whether player 1 will play A or B in a simultaneous game.
Q. How do you do Nash equilibrium?
To find the Nash equilibria, we examine each action profile in turn. Neither player can increase her payoff by choosing an action different from her current one. Thus this action profile is a Nash equilibrium. By choosing A rather than I, player 1 obtains a payoff of 1 rather than 0, given player 2’s action.
Q. What is a unique subgame perfect equilibrium?
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium) is a refinement of a Nash equilibrium used in dynamic games. Here one first considers the last actions of the game and determines which actions the final mover should take in each possible circumstance to maximize his/her utility.
Q. Can there be two SPNE?
More videos on YouTube Most games have only one subgame perfect equilibrium, but not all. When players receive the same payoff for two different strategies, they are indifferent and therefore may select either. This causes multiple SPE.
Q. Is SPNE always ne?
Notice that every SPNE must also be a NE, because the full game is also a subgame.
Q. What is first mover advantage in game theory?
In game theory, a player enjoys a first-mover advantage if he achieves a higher payoff by turning the game into a sequential one with him being the first mover, provided of course that the game can be changed in the first place.
Q. Who got the first mover advantage?
One possible explanation for Sony’s success is that its strong brand name, substantial financial resources, and excellent marketing skills allowed it to make the most of its first-mover status. But Xerox, too, had a great brand name, deep pockets, and many valuable skills.
Q. Is Netflix a first mover?
Netflix provides recommendations to viewers based on their own preferences and viewing history. First Mover Advantage: As Netflix was the first major player in the streaming industry they have managed to claim 30% of all Internet traffic in North America.
Q. What is the last mover advantage?
the advantage that a company has when it is the last to introduce a new product, service, or technology, because it can learn from developments that have taken place, or from what others have done: They took advantage of ever-accelerating advances in technology to capture what is called the last-mover advantage.