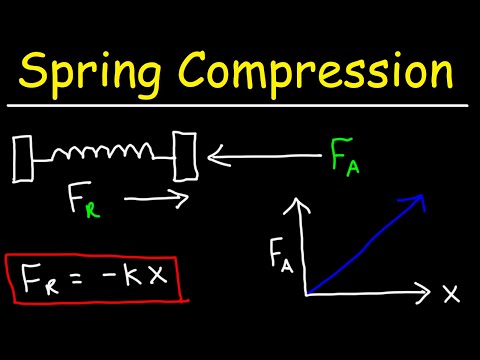
Work needed to compress a spring is the same as the potential energy stored in the compressed spring.
Q. What kind of energy is a compressed spring?
elastic potential energy
Q. What happens when a spring is compressed?
When you compress a spring, the potential energy is stored in the mechanical bonds between atoms, which you can think of as little springs. The spring as a whole can’t decompress – until it breaks – but little chunks can decompress as they come off. Most of the stored energy goes into decompressing each small part.
Q. Which type of energy is involved in stretching or compressing a spring?
Elastic potential energy
Q. Where is energy lost in a spring?
The energy goes into the thermal energy of the spring, the air around the block, or the block itself.
Q. What happens to the amount of potential energy stored in a spring as it is stretched?
Elastic potential energy increases with the constant of the spring and with the distance stretched.
Q. Does the spring constant depend on how far the spring is stretched?
More generally, the spring constant of a spring is inversely proportional to the length of the spring, assuming we are talking about a spring of a particular material and thickness. That means that the original mass of gm will only yield a stretch of mm on the shorter spring.
Q. What is a normal spring constant?
We have revealed that the spring constants of the nine CNCs, derived from the formula k = k’ δ’/δ, ranged from 0.9 N/m at the minimum to 4.8 N/m at the maximum. The average value for the nine CNCs was 1.8 N/m [15], which agrees with results previously reported [13].
Q. How do you find the maximum compression of a spring?
⇒F=kx , here F is the force applied by a spring having the spring constant k due to an extension x in the spring. Thus the maximum compression of the spring comes out to be equal to mak .
Q. Does the spring constant have a unit?
The units for the spring constant, k, are Newtons per meter (N/m).
Q. What is the spring constant a measure of?
stiffness
Q. What is spring constant and its unit?
The quantity that specifies the stiffness of a spring is called the spring constant. Every spring has its own natural value of spring constant. The letter k is used to denote the quantity. Its SI unit is Newton per meter (N/m). Basically, the spring works on the basis of Newton’s third law of motion.
Q. How do you find the mass and period of a spring constant?
Period of a Mass on a Spring. The period of a mass m on a spring of spring constant k can be calculated as T=2π√mk T = 2 π m k .
Q. What is the period T?
A period T is the time required for one complete cycle of vibration to pass a given point. As the frequency of a wave increases, the period of the wave decreases. Frequency and Period are in reciprocal relationships and can be expressed mathematically as: Period equals the Total time divided by the Number of cycles.
Q. How do you calculate the natural frequency of a spring mass?
Calculating the Natural Frequency The spring constant is measured in Newtons/meter. Springs with higher constants are stiffer and take more force to extend. In this case, the natural frequency is 1.6 Hz, which means the system would oscillate just over one and a half times per second.
Q. What is frequency of a spring?
The frequency of simple harmonic motion like a mass on a spring is determined by the mass m and the stiffness of the spring expressed in terms of a spring constant k ( see Hooke’s Law): If the period is T = s. then the frequency is f = Hz and the angular frequency = rad/s.
Q. How do you find the frequency of a spring?
The frequency f = 1/T = ω/2π of the motion gives the number of complete oscillations per unit time. It is measured in units of Hertz, (1 Hz = 1/s). a(t) = -ω2A cos(ωt + φ) = -ω2x. The quantity φ is called the phase constant.
Q. How do you find the resonant frequency of a spring?
The letter “m” stands for the mass of the spring, whereas “k” represents the spring constant, which can be given in a problem. Use the formula v = λf to find the resonance frequency of a single continuous wave. The letter “v” stands for the wave velocity, whereas “λ” represents the distance of the wavelength.
Q. How does spring constant affect frequency?
The natural resonant frequency of the oscillator can be changed by changing either the spring constant or the oscillating mass. Using a stiffer spring would increase the frequency of the oscillating system. The period is inversely proportional to the linear frequency.
Q. What happens when spring constant is increased?
A stronger spring-with a larger value of k-will move the same mass more quickly for a smaller period. As the spring constant k increases, the period decreases. For a given mass, that means a greater acceleration so the mass will move faster and, therefore, complete its motion quicker or in a shorter period.
Q. Can the spring constant change?
The proportional constant k is called the spring constant. When a spring is stretched or compressed, so that its length changes by an amount x from its equilibrium length, then it exerts a force F = -kx in a direction towards its equilibrium position.
Q. Does mass affect frequency of a spring?
As you can see the restoring force constant i.e. the spring constant does not depend on mass and hence the resulting motion Does depend on mass. Hence the natural frequency Does not depend on mass.
Q. Can a spring constant be negative?
The spring constant cannot be negative. The negative sign in Hooke’s law shows that the direction of the restoring force is opposite to the applied force.
Q. What happens to the period of a spring if the mass is doubled?
A mass attached to a spring vibrates with a period of 0.5 s. Thus, if the mass is doubled, the period increases by a factor of √2. A mass hanging from a spring is pulled down from its equilibrium position through a distance A and then released at t = 0. It oscillates with a frequency f.
Q. What is the relationship between spring constant and period?
The period of a spring-mass system is proportional to the square root of the mass and inversely proportional to the square root of the spring constant.
Q. Does Mass Affect period of oscillation?
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum does not depend on the mass of the bob. That means the resistance to changes in motion is directly proportional to the mass. However, the weight (a force) on an object is also proportional to mass.
Q. What is the relationship between mass and period of a pendulum?
The period of a pendulum does not depend on the mass of the ball, but only on the length of the string. Two pendula with different masses but the same length will have the same period. Two pendula with different lengths will different periods; the pendulum with the longer string will have the longer period.