Rabbits have many predators, and because of these predators the rabbit population is constantly levelingoff with births and deaths. So, predators and the food chain are what keeps the rabbit population in check.
Q. How will this impact the carrying capacity of the forest and the owl population within the forest?
How will this impact the carrying capacity of the forest and the owl population within the forest? The carrying capacity will decrease and the owl population will increase.
Table of Contents
- Q. How will this impact the carrying capacity of the forest and the owl population within the forest?
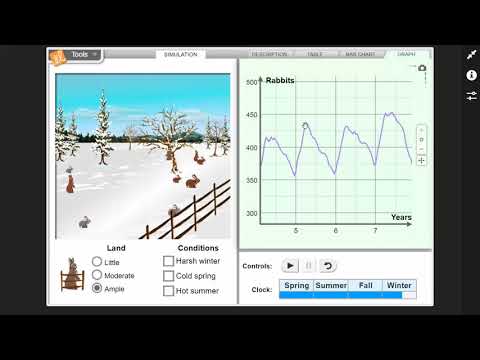
- Q. During which season does the rabbit population increase most rapidly?
- Q. What keeps the rabbit population in check?
- Q. What do rabbits need to stay alive and healthy?
- Q. How do harsh winters affect the rabbit population?
- Q. What is the most likely cause of the change in population size?
- Q. How do limiting factors most affect population size?
- Q. What are the biotic and abiotic factors that limit population size?
- Q. How can biotic and abiotic factors affect the size of a population?
- Q. How can abiotic factors affect the size of a population?
- Q. Under what circumstances can population growth be exponential?
- Q. Do limiting factors always decrease a population?
- Q. Which type of limiting factor affects a large population more than it affects a small population?
- Q. What type of limiting factor are predator/prey relationships?
- Q. Does a deeper wells mean better water?
- Q. Can a drilled well run dry?
- Q. Why would a drilled well go dry?
- Q. Does homeowners insurance cover well going dry?
- Q. Do wells run out of water?
- Q. What are the signs of a well going dry?
- Q. How much does it cost to replace a pump in a well?
- Q. Should you cover your well?
Q. During which season does the rabbit population increase most rapidly?
spring
- B.In which season did the rabbit population increase the least?
- oDuring the winter season the rabbit population decreased due to the cold weather conditions, which limited the rabbits chances of survival because there was not a large food supply available for them.
Q. What keeps the rabbit population in check?
Q. What do rabbits need to stay alive and healthy?
Pet rabbits need food, fresh water, a clean living space, and shelter from the elements in order to stay alive and healthy.
Q. How do harsh winters affect the rabbit population?
I think that a period of harsh winter will affect the rabbit population by reducing it because their will be a small food supply, and harsh weather conditions. Select Harsh winter from the CONDITIONSlisted on the SIMULATION pane. Click Play, and observe the how the population changes over five years.
Q. What is the most likely cause of the change in population size?
Changes in birth and death rates and migration all have an impact on whether the population of a region or country is increasing or decreasing. Changes in birth and death rates affect the natural increase or decrease of a population. Migration can also affect this along with the structure of the population.
Q. How do limiting factors most affect population size?
Limiting factors can lower birth rates, increase death rates, or lead to emigration. When organisms face limiting factors, they show logistic growth (S-shaped curve, curve B: Figure below). Competition for resources like food and space cause the growth rate to stop increasing, so the population levels off.
Q. What are the biotic and abiotic factors that limit population size?
Biotic or biological limiting factors are things like food, availability of mates, disease, and predators. Abiotic or physical limiting factors are non-living things such as temperature, wind, climate, sunlight, rainfall, soil composition, natural disasters, and pollution.
Q. How can biotic and abiotic factors affect the size of a population?
Biotic and abiotic factors determine the population size of a species in an ecosystem. Biotic factors include the amount of food that is available to that species and the number of organisms that also use that food source. …
Q. How can abiotic factors affect the size of a population?
Abiotic factors may include space, water, and climate. The carrying capacity of an environment is reached when the number of births equal the number of deaths. A limiting factor determines the carrying capacity for a species.
Q. Under what circumstances can population growth be exponential?
Exponential growth may occur in environments where there are few individuals and plentiful resources, but when the number of individuals becomes large enough, resources will be depleted, slowing the growth rate. Eventually, the growth rate will plateau or level off.
Q. Do limiting factors always decrease a population?
In the natural world, limiting factors like the availability of food, water, shelter and space can change animal and plant populations. Other limiting factors, like competition for resources, predation and disease can also impact populations. Other changes in limiting factors will cause a population to decrease.
Q. Which type of limiting factor affects a large population more than it affects a small population?
density dependent limiting factor
Q. What type of limiting factor are predator/prey relationships?
In the predator-prey example, one factor limits the growth of the other factor. As the prey population deceases, the predator population begins to decrease as well. The prey population is a limiting factor.
Q. Does a deeper wells mean better water?
In general, when it comes to water quality and well depth, there’s one golden rule: the deeper the well, the better the water quality. As you go deeper down, there’s a higher chance that the water you encounter will be rich in minerals.
Q. Can a drilled well run dry?
Does the well “running dry” do any damage? Yes, it can. Running the well pump when there isn’t water to pump can damage the pump itself which can cause it to burn out prematurely.
Q. Why would a drilled well go dry?
A well is said to have gone dry when water levels drop below a pump intake. This does not mean that a dry well will never have water in it again, as the water level may come back through time as aquifer recharge from precipitation seepage increases and/or pumping of the aquifer is lessened.
Q. Does homeowners insurance cover well going dry?
Generally, insurance will only cover a dry well if it ran dry because of an issue that is identified under your homeowner’s insurance policy. Insurance may make exceptions for “named perils” such as a fire, but it can also include volcanic activity, a collapsed sinkhole, or explosive events.
Q. Do wells run out of water?
Can Your Well Run Out of Water? If your well has been correctly drilled, it can last your family a lifetime, but it is possible for a well to run dry. This often happens with wells that are too shallow. If a well is not drilled deep enough, it may only be a water table well.
Q. What are the signs of a well going dry?
Warning Signs your Water Well may be Running Dry
- SIGNS YOUR WELL HAS RUN DRY.
- A Change In Taste.
- Murky or Muddy Water.
- Pump Runs Longer.
- Faucets Begin Sputtering.
- Neighbors Also Report Water Problems.
- HOW TO FIX A DRY WELL.
- HELPFUL TIPS.
Q. How much does it cost to replace a pump in a well?
The average cost of replacing a well pump is between $900 and $2,500. The cost varies based on the well size, materials used, and installation required. For example, replacing a shallow well pump will cost less than a deep well submersible pump.
Q. Should you cover your well?
DO NOT use any well coverings. Even though the sight of your wellhead may not be your favorite thing, you should not cover it up with any fake rocks, gravel, treated wood, or wishing wells.