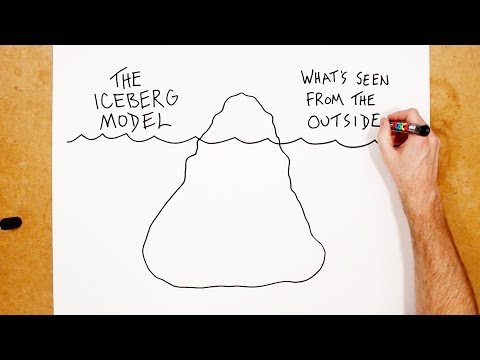
The iceberg model is a systems thinking tool designed to help an individual or group discover the patterns of behavior, supporting structures, and mental models that underlie a particular event. Source: Adapted from The Iceberg Model by M. Goodman, 2002.
Q. How do glaciers affect mountains?
Over hundreds of thousands of years, glaciers make many changes to the landscape. These slow-moving rivers of ice begin high on mountains. As they slide downhill, they carve deep, U-shaped valleys, sharp peaks, and steep ridges.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do glaciers affect mountains?
- Q. What happens when glaciers move?
- Q. How does a glacier move down a mountain valley?
- Q. How do glaciers erode mountains?
- Q. What does Safety T score mean?
- Q. What is a normal T score?
- Q. What do T scores tell you?
- Q. What do standard scores mean?
- Q. What does a standard score of 75 mean?
- Q. What does a standard score of 80 mean?
- Q. What does a standard score of 76 mean?
Q. What happens when glaciers move?
One component of glacier flow is the deformation of the ice itself. This happens at a microscopic scale, as movement occurs within and between individual ice crystals. They can slide past each other, break and deform, and recrystallize to form new grains.
Q. How does a glacier move down a mountain valley?
Gravity is the cause of glacier motion; the ice slowly flows and deforms (changes) in response to gravity. A glacier molds itself to the land and also molds the land as it creeps down the valley. Many glaciers slide on their beds, which enables them to move faster.
Q. How do glaciers erode mountains?
Glaciers erode the underlying rock by abrasion and plucking. Glacial meltwater seeps into cracks of the underlying rock, the water freezes and pushes pieces of rock outward. The rock is then plucked out and carried away by the flowing ice of the moving glacier (Figure below).
Q. What does Safety T score mean?
In this study, Safe T-Score method is used to analyze the accident rate by measuring the level of frequency. Analysis is continued using risk management methods which identify hazards, risk measurement and risk management.
Q. What is a normal T score?
A normal T-score falls between +1 and -1. Scores between -1 and -2.5 indicate low bone density, also called osteopenia. A T-score of -2.5 or lower indicates an established case of osteoporosis.
Q. What do T scores tell you?
A t-score (a.k.a. a t-value) is equivalent to the number of standard deviations away from the mean of the t-distribution. The t-score is the test statistic used in t-tests and regression tests. It can also be used to describe how far from the mean an observation is when the data follow a t-distribution.
Q. What do standard scores mean?
In statistics, the standard score is the number of standard deviations by which the value of a raw score (i.e., an observed value or data point) is above or below the mean value of what is being observed or measured.
Q. What does a standard score of 75 mean?
This means that your child performed as well as or better than 50 percent of children who are his age or in his grade. If your child earns a percentile rank of 75 on a standardized test, your child scored as well or better than 75 percent of his peers.
Q. What does a standard score of 80 mean?
• Classifying standard scores. Typically the normal limits of functioning encompass three classification categories: low average (standard scores of 80–89), average (standard scores of 90–110), and high average (111–120).
Q. What does a standard score of 76 mean?
76-84. High average. Normal limits; 68% of the population. 90-110. 25-75.