Urea is naturally produced when the liver breaks down protein or amino acids, and ammonia. The kidneys then transfer the urea from the blood to the urine. Extra nitrogen is expelled from the body through urea, and because it is extremely soluble, it is a very efficient process.
Q. How urea is formed from ammonium cyanate?
One of the bonds between the carbon and nitrogen form a bond with the nitrogen in the ammonia and one of the nitrogen hydrogen bonds forms with the other nitrogen, forming urea. Where ammonium cyanate was expected to form, it instead continues to react to surprisingly form urea.
Table of Contents
- Q. How urea is formed from ammonium cyanate?
- Q. Who first made urea?
- Q. Where does urea synthesis occur?
- Q. Is uric acid the same as urea?
- Q. How many amino acids take part in the urea cycle?
- Q. Where does urea cycle happen?
- Q. How many ATPS are used in urea cycle?
- Q. What amino acid makes urea?
- Q. Which organ produces most of the urea in the body?
- Q. Is urea toxic to the body?
- Q. What happens if blood urea is high?
- Q. What is the side effect of urea?
- Q. Is urea a protein?
- Q. What does Urea do to a protein?
- Q. What are examples of non protein nitrogen substances?
- Q. What is urea toxicity?
- Q. Why can’t urea get wet?
- Q. How does urea work in soil?
Q. Who first made urea?
Friedrich Wöhler
Q. Where does urea synthesis occur?
The liver is the only site where urea is synthesized and ultimately excreted by the kidneys.
Q. Is uric acid the same as urea?
Conversion of ammonia into uric acid is more energy intensive than the conversion of ammonia into urea. Producing uric acid instead of urea is advantageous because it is less toxic and reduces water loss and the subsequent need for water.
Q. How many amino acids take part in the urea cycle?
20 amino acids
Q. Where does urea cycle happen?
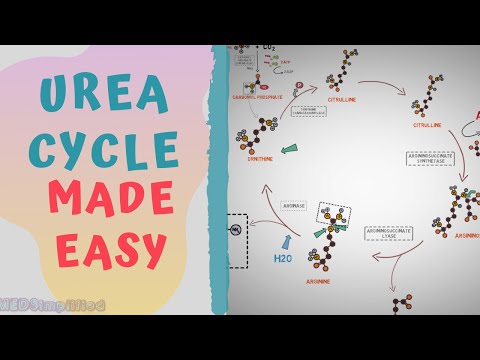
In humans and mammals, almost 80% of the nitrogen excreted is in the form of urea, which is produced through a series of reactions occurring in the cytosol and mitochondrial matrix of liver cells. These reactions are collectively called the urea cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit cycle.
Q. How many ATPS are used in urea cycle?
two ATP
Q. What amino acid makes urea?
The three amino acids found by Krebs and Henseleit to stimulate urea formation from ammonia in liver slices are boxed. As shown, ornithine and citrnlline can serve as successive precursors of arginine. Note that citrulline and ornithine are nonstandard amino acids that are not found in proteins.
Q. Which organ produces most of the urea in the body?
The liver produces several chemicals (enzymes) that change ammonia into a form called urea, which the body can remove in the urine.
Q. Is urea toxic to the body?
Urea can be irritating to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Repeated or prolonged contact with urea in fertilizer form on the skin may cause dermatitis. High concentrations in the blood can be damaging.
Q. What happens if blood urea is high?
High values A high BUN value can mean kidney injury or disease is present. Kidney damage can be caused by diabetes or high blood pressure that directly affects the kidneys. High BUN levels can also be caused by low blood flow to the kidneys caused by dehydration or heart failure. Many medicines may cause a high BUN.
Q. What is the side effect of urea?
Burning, itching, stinging, redness, or irritation may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Tell your doctor right away if any of these unlikely but serious side effects occur: unusual changes in the skin (e.g., blistering, peeling), signs of skin infection.
Q. Is urea a protein?
Urea is a non-protein nitrogen compound. Most urea contains about 45% nitrogen, and protein contains 16% nitrogen. Therefore, when urea is converted to protein, the crude protein equivalent value of urea is about 281%.
Q. What does Urea do to a protein?
It handles the disposal of excess nitrogen in the human body and acts as an agent in the denaturation of proteins. Urea belongs to a class of compounds known as chaotropic denaturants, which unravel the tertiary structure of proteins by destabilizing internal, non-covalent bonds between atoms.
Q. What are examples of non protein nitrogen substances?
Non-protein nitrogen compounds are urea (45%), free amino acids (16%), creatine (2.4%), creatinin (1.7%), ammonium nitrogen (1%), uric acid (2.1%), and other indeterminate compounds. Sheep’s milk contains more urea and uric acid than found in cow’s milk.
Q. What is urea toxicity?
Urea poisoning is one of the more commonly suspected toxicities of cattle in the Top End. The ammonia is then converted back to urea in the liver and is then excreted by the kidneys. This pathway can easily be overwhelmed when excess ammonia and urea circulate in the blood, causing poisoning.
Q. Why can’t urea get wet?
Urea is lost for the following reason. It reacts with water to form ammonium carbonate. However, if the urea is on the soil surface when the breakdown occurs, the ammonia gas is lost to the atmosphere. These losses can be greater if the soil has a high pH or if the soil is wet when the urea is applied.
Q. How does urea work in soil?
When urea is applied, an enzyme in soil and plant residue called urease quickly converts the urea into ammonia N. If this conversion occurs beneath the soil surface, the ammonia is converted to ammonium nitrogen and bound to soil particles.