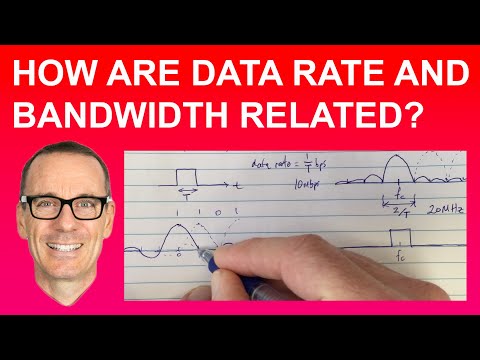
We need to upgrade a channel to a higher bandwidth. Answer the following questions: (a) How is the rate improved if we double the bandwidth? Clearly, by doubling the bandwidth (2B), the capacity (i.e. data rate) is doubled.
Q. What is maximum data rate of channel?
Higher data rates are expressed as Kbps (“Kilo” bits per second, i.e.1000 bps), Mbps (“Mega” bits per second, i.e.1000 Kbps), Gbps (“Giga” bits per second, i.e. 1000 Mbps) and Tbps (“Tera” bits per second, i.e. 1000 Gbps). One of the main objectives of data communications is to increase the data rate.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is maximum data rate of channel?
- Q. How is the rate improved if we double the SNR?
- Q. Is higher SNR better?
- Q. What is a good SNR ratio?
- Q. What is better high or low SNR?
- Q. How can I improve my SNR ratio?
- Q. How do you fix SNR problems?
- Q. How do you fix SNR margin?
- Q. What is an acceptable SNR margin?
- Q. Why is SNR margin low?
- Q. What does a low SNR mean?
- Q. How can I increase my MRI SNR?
- Q. What affects SNR margin?
- Q. What is an SNR reset?
- Q. Should noise margin be high or low?
- Q. How do you find SNR?
- Q. Why is SNR important?
- Q. What is the noise margin in logic gates related to?
- Q. What is standard TTL noise margin?
- Q. How the noise margin is affected by voltage scaling?
- Q. How noise margin NML of inverter can be improved?
- Q. Which has better noise margin?
- Q. Which is the most important parameter for designing of noise margin?
- Q. What is Noise Margin * 1 point?
- Q. What is fan in of a gate?
Q. How is the rate improved if we double the SNR?
b. How is the rate (capacity) improved if we double the SNR? When bandwidth is doubled the capacity of the channel is increased thus the number of bits sent also increases, the rate of the channel also increases or is doubled.
Q. Is higher SNR better?
To achieve a reliable connection, the signal level has to be significantly greater than the noise level. An SNR greater than 40 dB is considered excellent, whereas a SNR below 15 dB may result in a slow, unreliable connection.
Q. What is a good SNR ratio?
Generally, a signal with an SNR value of 20 dB or more is recommended for data networks where as an SNR value of 25 dB or more is recommended for networks that use voice applications. Learn more about Signal-to-Noise Ratio.
Q. What is better high or low SNR?
A higher SNR value means that the signal strength is stronger in relation to the noise levels, which allows higher data rates and fewer retransmissions – all of which offers better throughput. A lower SNR requires wireless LAN devices to operate at lower data rates, which decreases throughput.
Q. How can I improve my SNR ratio?
What is a Signal-to-Noise Ratio and how can I improve it?
- using high quality sensors and electronic devices in your camera.
- using a good electronic architecture when designing your camera.
- lowering the temperature of the sensor and the other analog devices in your camera.
Q. How do you fix SNR problems?
Fixing SNR Issues
- Remove Extra WiFi networks. This is especially true if this is a business environment.
- Check for “Noisy” devices. Take a look at the devices around the WiFi router.
- Turn off unneeded signals. Some routers support multiple bands in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz range.
Q. How do you fix SNR margin?
Luckily, there are some things you can do to improve the SNR margin:
- Buy a router that is good enough to manage low SNR margin figures.
- Install a good quality ADSL filter to your router and to each phone device installed on the same line.
- Try to change the ADSL provider, as some providers are less crowded than others.
Q. What is an acceptable SNR margin?
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) Typical values are: 10dB and lower is bad. 11db – 20dB is OK. 20dB – 28dB is excellent. 29dB and above is outstanding.
Q. Why is SNR margin low?
The most common problem on longer lines is that your SNR is too low to maintain a steady connection. For each upgrade between the speeds you can expect to lose on average 6dB. Therefore if you upgraded from 512kbps to 2Mbps then your SNR Margin is likely to have dropped in the region of 12dB.
Q. What does a low SNR mean?
If the SNR value gets lower than one, the signal becomes unusable. This is called the “noise floor.” This means that for a given signal level, an increase in noise will decrease the data throughput. The higher the noise level, the less space there is for the actual data that is being transmitted on the channel.
Q. How can I increase my MRI SNR?
In MRI, the signal-to-noise ratio can be improved by:
- volume acquisition as compared to 2D imaging, but imaging time is increased.
- spin-echo sequences as compared to gradient echo.
- decreasing the noise by reducing the bandwidth, using surface coils, and increasing the number of excitations.
Q. What affects SNR margin?
SNR = signal / noise , so higher signal, or/and lower noise would increase SNR. SNR margin = signal – noise (The difference between background noise and useful signal), so again, higher SNR margin also means that you have cleaner/stronger signal.
Q. What is an SNR reset?
Re: What does an SNR reset actually do? SNR does not “do” anything, its simply indicates how much margin is left, that could be used to carry extra information. The higher the SNR, the more stable the connection will be, but the speed will be lower.
Q. Should noise margin be high or low?
There are two noise margins we must consider, and they are as follows: noise margin high (NMH) and noise margin low (NML). The minimum voltage output of the driving device for a logic high (VOH min) must be larger than the minimum voltage input (VIH min) of the receiving device for a logical high.
Q. How do you find SNR?
For power spectrum SNR = (average signal power)/ average noise power), which in dB refers to (SNRdB=10 log10(SNR).
Q. Why is SNR important?
SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem.
Q. What is the noise margin in logic gates related to?
4 Noise Margins. The I/O noise margins, NML and NMH, refer to the ability of a logic gate to accommodate input noise without producing a faulty logic output. The input noise threshold levels, VIL and VIH, are by convention defined as the input voltages that result in a slope of −1 in the dVO/dVI response.
Q. What is standard TTL noise margin?
It should be obvious from these figures that CMOS gate circuits have far greater noise margins than TTL: 1.45 volts for CMOS low-level and high-level margins, versus a maximum of 0.7 volts for TTL.
Q. How the noise margin is affected by voltage scaling?
… As the supply voltage is reduced, the noise margin decreases as well [42] .
Q. How noise margin NML of inverter can be improved?
Figure 4 shows that the noise margin can be greatly improved by using dual gate transistors. The noise margin increases from about 0.5V for the single gate inverters to about 5.9V for the dual gate inverters.
Q. Which has better noise margin?
Noise margins for CMOS chips are usually much greater than those for TTL because the VOH min is closer to the power supply voltage and VOL max is closer to zero. Typically, in a CMOS inverter VOH will equal VDD and VOL will equal the ground potential, as mentioned above.
Q. Which is the most important parameter for designing of noise margin?
Static Noise Margin (SNM) is the most important parameter for memory design. SNM, which affects both read and write margin, is related to the threshold voltages of the NMOS and PMOS devices of the SRAM cell that is why we have analyzed SNM with the Read Margin, Write Margin and also the Threshold voltage.
Q. What is Noise Margin * 1 point?
Explanation: Noise Margin is defined as the amount of noise the logic circuit can withstand, it is given by the difference between VOH and VIH or VIL and VOL. Explanation: Noise margin = VOH – VIH.
Q. What is fan in of a gate?
Fan-in is the number of inputs a logic gate can handle. For instance the fan-in for the AND gate shown in the figure is 3. Physical logic gates with a large fan-in tend to be slower than those with a small fan-in. This is because the complexity of the input circuitry increases the input capacitance of the device.