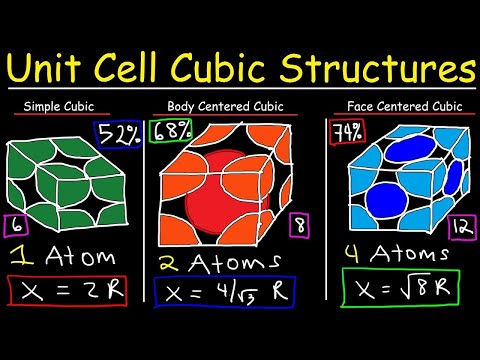
2 atoms
Q. Is BCC a primitive cell?
A primitive cell of the bcc lattice is shown in Fig. 11, and the primitive translation vectors are shown in Fig. 12. cells by definition contain only one lattice point, but the conventional bcc cell contains 2 lattice points, and the conventional fcc cell contains 4 lattice points.
Table of Contents
- Q. Is BCC a primitive cell?
- Q. What is the value of n in BCC?
- Q. How many lattice are there?
- Q. How many lattice points are in the unit cell?
- Q. What has lattice point only at the corner of the unit cell?
- Q. How do you find the lattice point?
- Q. What is the difference between lattice point and unit cell?
- Q. What is unit cell and its types?
- Q. What is unit cell and lattice?
- Q. What is the difference between lattice and crystal?
- Q. What are three dimensional lattices?
- Q. What are two dimensional lattices?
- Q. What are two dimensional defects?
- Q. What is the unit cell for the two dimensional structure?
- Q. Why is the simple hexagon not a two dimensional point lattice?
- Q. What are the types of unit cell?
- Q. How many different types of unit cells are possible for two dimensional lattices?
- Q. How many types of primitive unit cells are there?
- Q. What is unit cell parameters?
- Q. How many Bravais lattice are possible in three dimensions?
Q. What is the value of n in BCC?
The conventional unit cell contains 8 lattice points at the vertices, each being shared by 8 cells and another lattice point that is completely inside the conventional unit cell. So the number N of poitns per unit cell adds up to N=8⋅18+1=2.
Q. How many lattice are there?
The Bravais lattices
| Name | Number of Bravais lattices | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Tetragonal | 2 | a1 = a2 ¹ a3 a = b = g = 90° |
| Cubic | 3 | a1 = a2 = a3 a = b = g = 90° |
| Trigonal | 1 | a1 = a2 = a3 a = b = g < 120° ¹ 90° |
| Hexagonal | 1 | a1 = a2 ¹ a3 a = b = 90° g = 120° |
Q. How many lattice points are in the unit cell?
SO contribution of the lattice point in a unit cell by the corners=8×18=1 and at the point center it is 1 lattice point. So, the total number of lattice points contributed per unit cell=1+1=2. (i)Face-centered cubic is 4.
Q. What has lattice point only at the corner of the unit cell?
Answer: Primitive unit cells contain only one lattice point, which is made up from the lattice points at each of the corners. Non-primitive unit cells contain additional lattice points, either on a face of the unit cell or within the unit cell, and so have more than one lattice point per unit cell.
Q. How do you find the lattice point?
How do I calculate lattice points per unit volume? [duplicate]
- Simple Cubic: 8⋅1/8=1 lattice point per unit volume.
- Body Centered Cubic: (8⋅1/8)+1=2 lattice points per unit volume.
- Face Centered Cubic: (8⋅1/8)+(6⋅1/2)=4 lattice points per unit volume.
Q. What is the difference between lattice point and unit cell?
In three dimensions the unit cell is any parallelepiped whose vertices are lattice points, in two dimensions it is any parallelogram whose vertices are lattice points. Primitive unit cells contain only one lattice point, which is made up from the lattice points at each of the corners.
Q. What is unit cell and its types?
A unit cell is the smallest repeating portion of a crystal lattice. As one example, the cubic crystal system is composed of three different types of unit cells: (1) simple cubic , (2) face-centered cubic , and (3)body-centered cubic . These are shown in three different ways in the Figure below .
Q. What is unit cell and lattice?
The regular three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or ions in a crystal is usually described in terms of a space lattice and a unit cell. This parallel-sided figure is the unit cell. It represents the simplest, smallest shape from which the overall structure can be constructed.
Q. What is the difference between lattice and crystal?
Crystalline material consists of a regular repetition of a group of atoms in three dimensional space. A crystal lattice is an infinitely repeating array of points in space .
Q. What are three dimensional lattices?
The simplest three-dimensional lattice is the simple cubic lattice, COn- sisting of points evenly spaced along all three axes, R = (Cd, md, nd) for integers C, m, and n, with lattice spacing d. The primitive unit cell is a cube of side d centered on each lattice point, with volume d3 .
Q. What are two dimensional lattices?
… the two-dimensional lattices are organized into five types called Bravais lattices. The relationships in the length |a|,|b| and the angle φ between two lattice vectors are as follows: For the rectangular lattice, two types of unit cell can be defined, as shown in figure 1. …
Q. What are two dimensional defects?
What are two-dimensional defects? a) Boundary defectb) Point defectc) Line defectd) Volume defectView AnswerAnswer: aExplanation: The defects that occur on the surface of a material are known as surface or boundary defects. Geometrically, they are regarded as two-dimensional defects.
Q. What is the unit cell for the two dimensional structure?
(a) In a crystalline solid there is a relatively small repeating unit called a unit cell that is made up of a unique arrangement of atoms and embodies the structure of the solid. (b) The two dimensional lattices are square.
Q. Why is the simple hexagon not a two dimensional point lattice?
We cannot represent all crystal systems as dimensional point lattice. The crystal lattice of hexagonal system is as follows: In simple hexagon for two dimensional point lattice it may show cubic or orthorhombic lattice. That’s why simple hexagon is not a two dimensional point lattice.
Q. What are the types of unit cell?
There are three types of unit cells present in nature, primitive cubic, body-centered cubic, and face-centered cubic.
Q. How many different types of unit cells are possible for two dimensional lattices?
There are seven types of unit cell formed. These are Cubic, Tetragonal, Orthorhombic, Monoclinic, Hexagonal, Rhombohedral or Trigonal and Triclinic.
Q. How many types of primitive unit cells are there?
How many kinds of primitive unit cells are possible? Seven simple crystal structures exist; cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, hexagonal, monoclinical, triclinical, and rhomboedral. They differ in the way their crystallographic axes and angles are arranged.
Q. What is unit cell parameters?
The unit cell is defined as the smallest repeating unit having the full symmetry of the crystal structure. The geometry of the unit cell is defined as a parallelepiped, providing six lattice parameters taken as the lengths of the cell edges (a, b, c) and the angles between them (α, β, γ).
Q. How many Bravais lattice are possible in three dimensions?
14