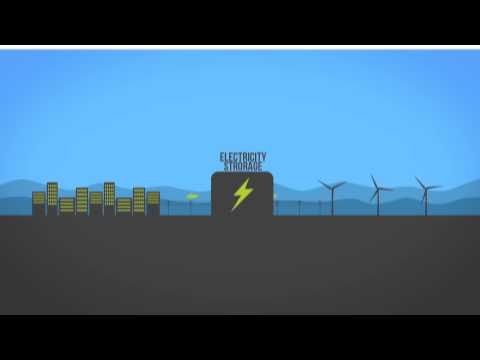
Electricity cannot itself be stored on any scale, but it can be converted to other forms of energy which can be stored and later reconverted to electricity on demand. Storage systems for electricity include battery, flywheel, compressed air, and pumped hydro storage.
Q. What are 5 types of energy transfer?
What are the different ways that energy can be transferred?
Table of Contents
- Q. What are 5 types of energy transfer?
- Q. What is energy How many types of energy?
- Q. What are the three forms of energy transfer?
- Q. What are the four pathways for transferring energy?
- Q. What are the two differences between free and forced convection?
- Q. What is difference between natural and forced convection give examples?
- Q. What causes natural convection?
- Q. What is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms Class 7?
- Q. Which of the following is the greatest source of energy?
- Q. Which type of energy is used by living organisms?
- Q. What is the most important type of energy for living organisms?
- Q. What type of energy do humans have?
- Q. What type of energy does a fan use?
- Conduction: Heat is thermal energy, and in solids it can be transferred by conduction. Heat is passed along from the hotter end of an object to the cold end by the particles in the solid vibrating.
- Convection: Fluids, that is both gases and liquids, can transfer heat energy by convection.
- Radiation:
Q. What is energy How many types of energy?
6 Forms
About Energy Transfers
- Mechanically – By the action of a force.
- Electrically – By an electrical current.
- By radiation – By Light waves or Sound waves.
- By heating – By conduction, convection or radiation.
Q. What are the three forms of energy transfer?
Heat can be transferred in three ways: by conduction, by convection, and by radiation.
- Conduction is the transfer of energy from one molecule to another by direct contact.
- Convection is the movement of heat by a fluid such as water or air.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves.
Q. What are the four pathways for transferring energy?
There are four main pathways: mechanical work – a force moving an object through a distance. electrical work – charges moving due to a potential difference. heating – due to temperature difference caused electrically or by chemical reaction.
Q. What are the two differences between free and forced convection?
Free convection: If the motion of the fluid is only due to its density difference because of temperature variation, then it is free convection. Forced convection: In this mode of heat transfer some external source like blower is used to cause the motion of the air.
Q. What is difference between natural and forced convection give examples?
In natural convection, no external factors affect the heat transfer. In forced convection, only external factors affect heat transfer. For example: Heated plate when kept in atmosphere gets cooled by air is natural convection. For example: Heated plate when kept under a fan for cooling is forced way of convection..
Q. What causes natural convection?
Natural convection arises from temperature differences among air parcels, or heat transfer at surfaces (i.e. surface-to-air temperature difference). In the absence of forced convection, natural convection becomes the only means of air mixing inside enclosed spaces.
Q. What is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms Class 7?
Sun
Q. Which of the following is the greatest source of energy?
Oil has been historically the world’s most used energy source accounting for approximately 39% of the global energy consumption.
Q. Which type of energy is used by living organisms?
Chemical energy
Q. What is the most important type of energy for living organisms?
Heat, or thermal energy, is a form of kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules. Light is another kind of KE that can be harnessed to perform work. It is the most important type of energy for living organisms – it is the energy that is available to do the work of the cell.
Q. What type of energy do humans have?
When we go for a run we are using chemical energy in our bodies to produce movement (kinetic energy), which in turn converts to warmth (thermal energy).
Q. What type of energy does a fan use?
The fan converts electric energy into kinetic energy that does work, and it converts some electric energy into heat.)