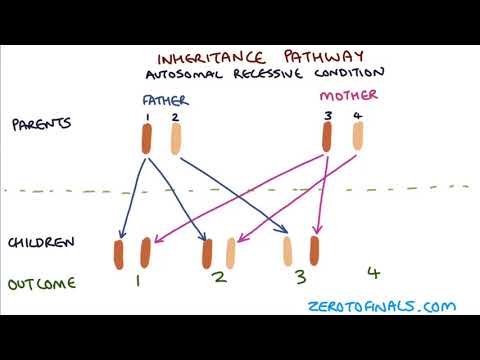
In a pedigree chart, the circle represents a female and a square represents a male. A vertical line connects the parents to children. Horizontal line represents a male and a female are married. Shaded parts show dominant traits and non shaded parts show recessive traits.
Q. What do the circles represent on a pedigree?
In a pedigree, a circle represents a female, and a square represents a male. A filled-in circle or square shows that the individual has the trait being studied.
Table of Contents
- Q. What do the circles represent on a pedigree?
- Q. How do you know a pedigree is dominant or recessive?
- Q. How many generations are shown in this pedigree?
- Q. Are circles males or females?
- Q. How are the next generations represented in a pedigree chart?
- Q. How do you tell if a pedigree is autosomal or Sexlinked?
- Q. Is Klinefelter syndrome autosomal or Sexlinked?
- Q. How can you tell the difference between dominant and autosomal recessive?
- Q. How do you know if something is autosomal dominant?
- Q. What are examples of autosomal dominant disorders?
- Q. How do you explain autosomal dominant inheritance?
- Q. What is meant by autosomal dominant?
- Q. What are the characteristics of autosomal recessive inheritance?
- Q. What are some examples of autosomal recessive disorders?
- Q. How do you know if something is autosomal recessive?
- Q. What are two key characteristics of an autosomal recessive trait?
- Q. What is the meaning of autosomal recessive trait?
- Q. What are some recessive traits?
- Q. Is height a dominant or recessive trait?
- Q. What is the most common recessive trait?
- Q. What determines if a genetic trait is expressed?
Q. How do you know a pedigree is dominant or recessive?
If both parents do not have the trait and the child does, it is recessive. If one parent has the trait and the child does or does not, it is dominant.
Q. How many generations are shown in this pedigree?
(7.4) Pedigree flashcards
| A | B |
|---|---|
| How many generations are shown on this pedigree?, | 3 generations are shown. |
| Which individual is a female affected by the trait of interest?, | I-2 is the affected female. |
| Which individual is a male affected by the trail of interest?, | III-2 is the affected male. |
Q. Are circles males or females?
The use of shapes as gender symbols may have originated from kinship diagrams in anthropology, where a circle represents a female and a triangle represents a male.
Q. How are the next generations represented in a pedigree chart?
Each generation is identified by a Roman numeral (I, II, III, and so on), and each individual within the same generation is identified by an Arabic numeral (1, 2, 3, and so on).
Q. How do you tell if a pedigree is autosomal or Sexlinked?
Explanation:
- In a pedigree displaying autosomal trait, affected individuals are of both sex: that is both male and female individuals could be affected in 1:1 ratio.
- In a pedigree displaying sex linked trait, an overwhelming number of males will be affected.
Q. Is Klinefelter syndrome autosomal or Sexlinked?
Understanding Autosomal And Sex Linked Inheritance : Example Question #6. Individuals with Klinefelter syndrome are phenotypically male, but experience reduced sperm production and breast development in adolescence. Klinefelter individuals have two X-chromosomes and one Y-chromosome (they are XXY instead of XY).
Q. How can you tell the difference between dominant and autosomal recessive?
“Autosomal” means that the gene in question is located on one of the numbered, or non-sex, chromosomes. “Dominant” means that a single copy of the disease-associated mutation is enough to cause the disease. This is in contrast to a recessive disorder, where two copies of the mutation are needed to cause the disease.
Q. How do you know if something is autosomal dominant?
If it is a 50/50 ratio between men and women the disorder is autosomal. Determine whether the disorder is dominant or recessive. If the disorder is dominant, one of the parents must have the disorder. they can be heterozygous.
Q. What are examples of autosomal dominant disorders?
Examples of autosomal dominant diseases include Huntington disease, neurofibromatosis, and polycystic kidney disease.
Q. How do you explain autosomal dominant inheritance?
Autosomal dominant inheritance is a way a genetic trait or condition can be passed down from parent to child. One copy of a mutated (changed) gene from one parent can cause the genetic condition. A child who has a parent with the mutated gene has a 50% chance of inheriting that mutated gene.
Q. What is meant by autosomal dominant?
Q. What are the characteristics of autosomal recessive inheritance?
To have an autosomal recessive disorder, you inherit two mutated genes, one from each parent. These disorders are usually passed on by two carriers. Their health is rarely affected, but they have one mutated gene (recessive gene) and one normal gene (dominant gene) for the condition.
Q. What are some examples of autosomal recessive disorders?
Examples of autosomal recessive disorders include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease.
Q. How do you know if something is autosomal recessive?
One trick for identifying a recessive trait is that if a trait skips a generation in a pedigree, it is often an autosomal recessive trait (although a trait can be autosomal recessive and not skip generations). These traits appear with equal frequency in both sexes.
Q. What are two key characteristics of an autosomal recessive trait?
A 50% chance that the child is born with one normal and one abnormal gene (carrier, without disease) A 25% chance that the child is born with two abnormal genes (at risk for the disease)
Q. What is the meaning of autosomal recessive trait?
Autosomal recessive inheritance is a way a genetic trait or condition can be passed down from parent to child. A genetic condition can occur when the child inherits one copy of a mutated (changed) gene from each parent. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive condition usually do not have the condition.
Q. What are some recessive traits?
Examples of Recessive Traits For example, having a straight hairline is recessive, while having a widow’s peak (a V-shaped hairline near the forehead) is dominant. Cleft chin, dimples, and freckles are similar examples; individuals with recessive alleles for a cleft chin, dimples, or freckles do not have these traits.
Q. Is height a dominant or recessive trait?
For example, the gene for having an extra finger is actually dominant, while the gene for having a tall stature is a recessive trait.
Q. What is the most common recessive trait?
Thus, majority of the people have inherited the dominant gene resulting in right-handedness. The gene for naturally curly hair is dominant and the gene for straight hair is recessive….Common Dominant And Recessive Traits.
| Dominant Trait in Humans | Recessive Trait in Humans |
|---|---|
| Broad nose | Narrow nose |
| Dwarfism | Normal growth |
| Hazel or green eyes | Blue or gray eyes |
Q. What determines if a genetic trait is expressed?
Diploid organisms inherit two alleles for each gene; one allele from each parent. Interactions between alleles determine an organism’s phenotype. If an organism inherits two of the same alleles for a particular trait, it is homozygous for that trait. In co-dominace relationships, both alleles are fully expressed.