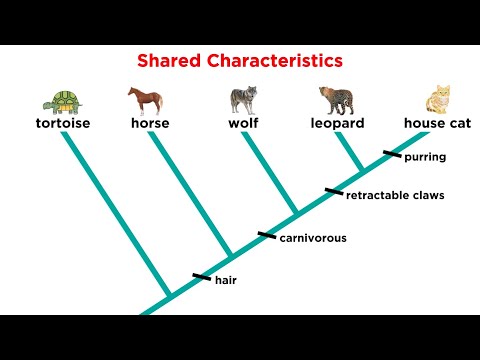
To determine how closely related two organisms on a cladogram are, TRACE from the first one to the second one. The more nodes you pass, the farther apart the organisms are in terms of evolutionary relationship.
Q. What can you learn from a Cladogram?
Biologists use cladograms and phylogenetic trees to illustrate relationships among organisms and evolutionary relationships for organisms with a shared common ancestor. Both cladograms and phylogenetic trees show relationships among organisms, how alike, or similar, they might be.
Table of Contents
- Q. What can you learn from a Cladogram?
- Q. Which two organisms on the Cladogram are the most closely related?
- Q. What type of evidence is the best indicator of how closely two species are related?
- Q. Which of the following would be considered the strongest evidence that two species are related?
- Q. Why do humans dogs and birds all have similar bones in their forelimbs and hands?
- Q. Which bones do humans and tetrapods share?
- Q. What is homologous organ and analogous organ?
- Q. Is a whale homologous or analogous?
Q. Which two organisms on the Cladogram are the most closely related?
Why? Worms and spiders are more closely related. They have more traits in common.
Q. What type of evidence is the best indicator of how closely two species are related?
The best evidence is similarities in DNA and protein structures. By studying DNA and protein structures we can see genetic information and the position of amino acids in its sequence of proteins. Studying the similarities between organisms’ protein structures, we can see how closely they are related.
Q. Which of the following would be considered the strongest evidence that two species are related?
Similar DNA sequences are the strongest evidence for evolution from a common ancestor. More similarities in the DNA sequence is evidence for a closer evolutionary relationship. Look at the cladogram in the Figure below. It shows how humans and apes are related based on their DNA sequences.
Q. Why do humans dogs and birds all have similar bones in their forelimbs and hands?
The forelimbs of all mammals have the same basic bone structure. The structures are similar because they evolved to do the same job, not because they were inherited from a common ancestor. For example, the wings of bats and birds, shown in Figure below, look similar on the outside. They also have the same function.
Q. Which bones do humans and tetrapods share?
This 350 million year old animal, the first tetrapod, had limbs with one long bone (the humerus) attached to two other long bones (the radius and ulna). Its descendants, including whales, lizards, humans, and birds, as well as many others, inherited the tetrapod limb from this ancestor.
Q. What is homologous organ and analogous organ?
Homologous organs have similar origin n basic structure but perform different functions in different organisms. Analogous organs are different in basic structure but perform same functions. Homologous organs show divergent evolution. Analogous organs show convergent evolution. They develop in related organisms.
Q. Is a whale homologous or analogous?
Homologous structures are similar physical features in organisms that share a common ancestor, but the features serve completely different functions. An example of homologous structures are the limbs of humans, cats, whales, and bats.