Frequency (spikes/s) of the most active neuron A (S neuron in this case). Frequency (spikes/s) of the least active neuron fB= f – fA (W neuron in this case).
Q. Which of these ions is actively transported through the cell membrane to establish a resting potential quizlet?
A neuron that has as its primary function the job of connecting other neurons is called a(n) ________. Which of these ions is actively transported through the cell membrane to establish a resting potential? The sodium-potassium pump______.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of these ions is actively transported through the cell membrane to establish a resting potential quizlet?
- Q. What is the first step during an action potential?
- Q. What starts an action potential?
- Q. What happens during depolarization in an action potential?
- Q. How can you increase the frequency of an action potential?
- Q. What is the frequency of action potentials?
- Q. What limits the frequency of the action potentials?
- Q. What limits the frequency of action potentials quizlet?
- Q. Why does the frequency of action potentials increase when stimulus intensity increases?
- Q. What effect will the increased stimulus intensity have on the frequency of action potentials quizlet?
- Q. What is the relationship between the Interspike and the frequency of action potentials?
- Q. When the stimulus intensity is increased what changes the number?
- Q. Why does the stimulus intensity affect the amount of?
- Q. Why does the stimulus intensity affect the amount quizlet?
- Q. What will happen if you apply a strong stimulus to the sensory receptor?
- Q. What information does the brain use to determine the intensity of a stimulus?
- Q. How do sensory receptors communicate a stimulus to the brain?
- Q. Are sensory receptors located in blood vessels?
- Q. What type of stimulus is detected by the sensory receptors of the skin?
- Q. Which body locations typically lack Proprioceptors?
- Q. What is the role of the Na K pump in relation to the resting membrane potential?
- Q. Is depolarization excitatory or inhibitory?
- Q. Does depolarization mean contraction?
- Q. What maintains the resting membrane potential of a neuron quizlet?
- Q. What happens if you block sodium potassium pump?
- Q. What are the 4 types of ion channels?
- Q. What is responsible for the opening and closing of ion channel?
- Q. What is the major role of the Na +- K+ pump in maintaining the resting membrane potential view available hint’s What is the major role of the Na +- K+ pump in maintaining the resting membrane potential making the membrane potential negative by moving more Na+ ions?
- Q. Why is the Na K pump so important?
- Q. Which of the following will change the equilibrium potential for Na+?
- Q. Which ions play key roles in establishing and maintaining the resting membrane potential?
- Q. What is the most important factor in setting the resting membrane potential?
- Q. Which ion gives the greatest contribution to resting membrane potential and why?
- Q. What happens during resting membrane potential?
Q. What is the first step during an action potential?
When the membrane potential of the axon hillock of a neuron reaches threshold, a rapid change in membrane potential occurs in the form of an action potential. This moving change in membrane potential has three phases. First is depolarization, followed by repolarization and a short period of hyperpolarization.
Q. What starts an action potential?
Action potentials are caused when different ions cross the neuron membrane. A stimulus first causes sodium channels to open. Because there are many more sodium ions on the outside, and the inside of the neuron is negative relative to the outside, sodium ions rush into the neuron.
Q. What happens during depolarization in an action potential?
During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming positively charged. The opposite of a depolarization is called a hyperpolarization.
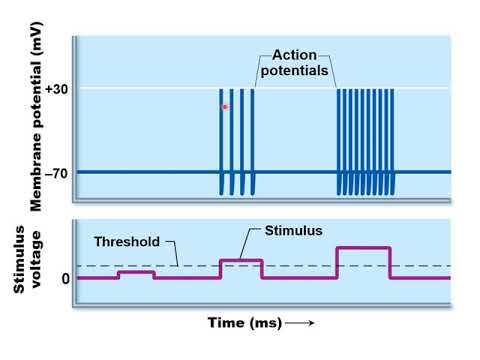
Q. How can you increase the frequency of an action potential?
Rather, the frequency or the number of action potentials increases. In general, the greater the intensity of a stimulus, (whether it be a light stimulus to a photoreceptor, a mechanical stimulus to the skin, or a stretch to a muscle receptor) the greater the number of action potentials elicited.
Q. What is the frequency of action potentials?
Whether saltatory or not, the mean conduction velocity of an action potential ranges from 1 meter per second (m/s) to over 100 m/s, and, in general, increases with axonal diameter. Action potentials cannot propagate through the membrane in myelinated segments of the axon.
Q. What limits the frequency of the action potentials?
(20 points) What limits the frequency at which action potentials can be generated ? Explain your answer. The absolute and relative refractory periods limit AP freq. Because the Na channels are closed during the absolute refractory period no new Aps can be generated so this represents the maximum freq.
Q. What limits the frequency of action potentials quizlet?
What limits the frequency of action potentials? The frequency of action potentials is limited by the strength of the stimulus and the refractory periods.
Q. Why does the frequency of action potentials increase when stimulus intensity increases?
Why does the frequency of action potentials increase when the stimulus intensity increases? Action potential can occur more frequently if there is a constant source of stimulation as long as the relative refractory period is reached.
Q. What effect will the increased stimulus intensity have on the frequency of action potentials quizlet?
Predict Question: What effect will the increased stimulus intensity have on the frequency of action potential? the frequency of action potential will decrease.
Q. What is the relationship between the Interspike and the frequency of action potentials?
What is the relationship between the interspike interval and the frequency of action potentials? The frequency of the action potentials is the reciprocal of the interspike interval with a conversion from milliseconds to seconds.
Q. When the stimulus intensity is increased what changes the number?
Chemical Synaptic Transmission & Neurotransmitter Release
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| When the stimulus intensity is increased, what changes: the number of synaptic vesicles released or the amount of neurotransmitter per vesicle? | The number os synaptic vesicles released increases when the stimulus intensity is increased. |
Q. Why does the stimulus intensity affect the amount of?
Why does the stimulus intensity affect the amount of neurotransmitter release at the axon terminal? Exocytosis of the synaptic vesicles is calcium dependent. When the stimulus intensity is increased, the number of synaptic vesicles increases.
Q. Why does the stimulus intensity affect the amount quizlet?
both “the stimulus intensity directly affects the amount the calcium entering the axon terminal.” and “the stimulus intensity proportionally affects the number of synaptic vesicles that discharge their contents into the synaptic cleft.”
Q. What will happen if you apply a strong stimulus to the sensory receptor?
A strong stimulus recruits more sensory receptors, compared to a weak stimulus. Identify the type of membrane potential (graded receptor potential or action potential) that occurred at R1, R2, R3, and R4 when you applied a moderate stimulus (view Experiment Results to view the response to this stimulus).
Q. What information does the brain use to determine the intensity of a stimulus?
How does the brain determine the intensity of a stimulus? By looking at the number of receptors activated and the frequency of action potentials from them. Also looks at the quality of the receptors that are activated. Receptors have different thresholds of activation – this can tell us how large the stimulus was.
Q. How do sensory receptors communicate a stimulus to the brain?
Sensory signals are converted to electrical signals via depolarization of sensory neuron membranes upon stimulus of the receptor, which causes opening of gated ion channels that cause the membrane potential to reach its threshold.
Q. Are sensory receptors located in blood vessels?
These are sensory receptors that are located in blood vessels and visceral organs and their signals are not usually consciously perceived. This type of sensory receptor responds to stimuli resulting from physical or chemical damage to tissue.
Q. What type of stimulus is detected by the sensory receptors of the skin?
Our skin includes touch and temperature receptors, and our inner ears contain sensory mechanoreceptors designed for detecting vibrations caused by sound or used to maintain balance.
Q. Which body locations typically lack Proprioceptors?
The body locations that typically lack proprioceptors are the skin, mainly the skin surface. This is because proprioceptors respond to stimuli deep in the body that help to identify the position and movement of the body. The skin is not involved in this process. Instead, the skin is home to numerous touch receptors.
Which of these ions is actively transported through the cell membrane to establish a resting potential? The sodium-potassium pump______. The synaptic cleft prevents an impulse from being transmitted directly from one neuron to another.
Q. What is the role of the Na K pump in relation to the resting membrane potential?
[3][4] The Na+K+-ATPase pump helps to maintain osmotic equilibrium and membrane potential in cells. The sodium and potassium move against the concentration gradients. The Na+ K+-ATPase pump maintains the gradient of a higher concentration of sodium extracellularly and a higher level of potassium intracellularly.
Q. Is depolarization excitatory or inhibitory?
This depolarization is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) and makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. Release of neurotransmitter at inhibitory synapses causes inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic membrane.
Q. Does depolarization mean contraction?
Depolarization does not mean contraction. Depolarization is a process where a cell’s membrane potential becomes more positive.
Q. What maintains the resting membrane potential of a neuron quizlet?
What normally maintains the resting membrane potential of a neuron during the resting state? The resting membrane potential is maintained by the distribution of positive and negative charges from sodium, potassium, proteins and other charged ions on either side of the neuronal membrane.
Q. What happens if you block sodium potassium pump?
The sodium pump is by itself electrogenic, three Na+ out for every two K+ that it imports. So if you block all sodium pump activity in a cell, you would see an immediate change in the membrane potential because you remove a hyperpolarizing current, in other words, the membrane potential becomes less negative.
Q. What are the 4 types of ion channels?
There are three main types of ion channels, i.e., voltage-gated, extracellular ligand-gated, and intracellular ligand-gated along with two groups of miscellaneous ion channels.
Q. What is responsible for the opening and closing of ion channel?
Most ion channels are gated—that is, they open and close either spontaneously or in response to a specific stimulus, such as the binding of a small molecule to the channel protein (ligand-gated ion channels) or a change in voltage across the membrane that is sensed by charged segments of the channel protein (voltage- …
Q. What is the major role of the Na +- K+ pump in maintaining the resting membrane potential view available hint’s What is the major role of the Na +- K+ pump in maintaining the resting membrane potential making the membrane potential negative by moving more Na+ ions?
What is the value for the resting membrane potential for most neurons? The Na+-K+ pump actively transports both sodium and potassium ions across the membrane to compensate for their constant leakage.
Q. Why is the Na K pump so important?
In the kidneys the sodium potassium pump helps to maintain the sodium and potassium balance. It also plays a role in maintaining blood pressure and control cardiac contractions. Failure of sodium potassium pump can result in the swelling of the cell.
Q. Which of the following will change the equilibrium potential for Na+?
The concentration of Na+ ion is higher outside the cell while it is lower inside the cell while the concentration of K+ ion is higher on the inner side of the cell as compared to the outer side of the cell. The ion gate is responsible for maintain this equilibrium.
Q. Which ions play key roles in establishing and maintaining the resting membrane potential?
Sodium, potassium, and chloride ions are present in the highest concentrations and therefore generally play the most important roles in the generation of the resting membrane potential.
Q. What is the most important factor in setting the resting membrane potential?
Typically, the amount of certain potassium channels is most important for control of the resting potential (see below). Some ion pumps such as the Na+/K+-ATPase are electrogenic, that is, they produce charge imbalance across the cell membrane and can also contribute directly to the membrane potential.
Q. Which ion gives the greatest contribution to resting membrane potential and why?
K+
Q. What happens during resting membrane potential?
What generates the resting membrane potential is the K+ that leaks from the inside of the cell to the outside via leak K+ channels and generates a negative charge in the inside of the membrane vs the outside. At rest, the membrane is impermeable to Na+, as all of the Na+ channels are closed.