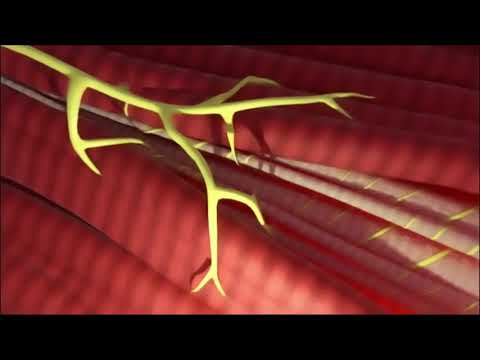
Spindle fibers move chromosomes during cell division by attaching to chromosome arms and centromeres. Kinetochore fibers and spindle polar fibers work together to separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. Spindle fibers that don’t contact chromosomes during cell division extend from one cell pole to the other.
Q. What is the main function of spindle fibers?
Spindle fibers form a protein structure that divides the genetic material in a cell. The spindle is necessary to equally divide the chromosomes in a parental cell into two daughter cells during both types of nuclear division: mitosis and meiosis. During mitosis, the spindle fibers are called the mitotic spindle.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the main function of spindle fibers?
- Q. What happens if spindle fibers don’t form?
- Q. What are the spindle fibers made of?
- Q. What do spindle fibers attach to?
- Q. What do the spindle fibers attach to in order to pull apart the sister chromatids?
- Q. What is a spindle and what is its function?
- Q. Are microtubules and spindle fibers the same?
- Q. What is the difference between spindle fibers and achromatic spindle?
- Q. What do spindle fibers do in mitosis?
- Q. What are the 4 functions of microtubules?
- Q. What is the main function of a microtubules?
- Q. What is the similarities and differences of microtubules and microfilaments?
- Q. What is the main function of microtubules in cells?
- Q. What are the 3 functions of microtubules?
- Q. What is ribosome Class 9?
Q. What happens if spindle fibers don’t form?
Spindle fiber formation occurs but spindle fibers cannot function properly, i.e. they cannot separate the daughter chromosomes in the division process. Chromosomes clump in several areas of the cell rather than along the single metaphase plate. Mitosis is disrupted and growth increases.
Q. What are the spindle fibers made of?
microtubules
Q. What do spindle fibers attach to?
centromere
Q. What do the spindle fibers attach to in order to pull apart the sister chromatids?
Spindle fibers from one side of the cell attach to one of the sister chromatids. The spindle fibers from the other side of the cell attach to the other sister chromatids of the chromosome. They attach at a point called the kinetochore, which is a disk or protein that is on each side of the centromere.
Q. What is a spindle and what is its function?
Q. Are microtubules and spindle fibers the same?
They are the same thing. As the others have written, microtubules are a “track” that can move organelles around when “motor” proteins (that cleave ATP) pull those organelles. The spindle is what moves the chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. Spindle fibers are used in cell division, and are made of microtubules.
Q. What is the difference between spindle fibers and achromatic spindle?
Answer. Explanation: they are different because spindle fibre arose from the centrioles . Achromatic fibre arose in cytoplasm and are elastic in nature.
Q. What do spindle fibers do in mitosis?
Q. What are the 4 functions of microtubules?
Intracellular organization. Microtubules are part of the cytoskeleton, a structural network within the cell’s cytoplasm. The roles of the microtubule cytoskeleton include mechanical support, organization of the cytoplasm, transport, motility and chromosome segregation.
Q. What is the main function of a microtubules?
Microtubules are filamentous intracellular structures that are responsible for various kinds of movements in all eukaryotic cells. Microtubules are involved in nucleic and cell division, organization of intracellular structure, and intracellular transport, as well as ciliary and flagellar motility.
Q. What is the similarities and differences of microtubules and microfilaments?
Comparison chart
| Microfilaments | Microtubules | |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Micro-filaments are smaller and thinner and mostly help cells move | Microtubules are shaped similarly but are larger, and help with cell functions such as mitosis and various cell transport functions. |
Q. What is the main function of microtubules in cells?
Microtubules are conveyer belts inside the cells. They move vesicles, granules, organelles like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are linear polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.
Q. What are the 3 functions of microtubules?
Functions of Microtubules
- Giving shape to cells and cellular membranes.
- Cell movement, which includes a contraction in muscle cells and more.
- Transportation of specific organelles within the cell via microtubule “roadways” or “conveyor belts.”
Q. What is ribosome Class 9?
Ribosomes are the cell organelles found inside the cell and composed of RNA and Proteins. They may found suspended in the cytosol, called free ribosomes or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum, called bound ribosomes. They help in protein synthesis.