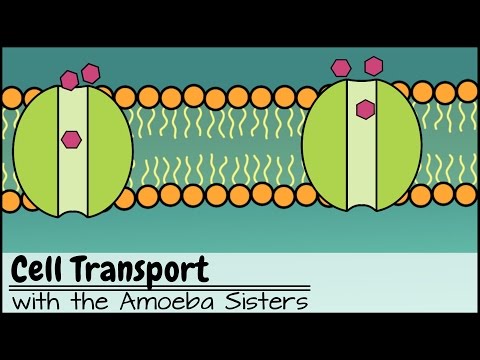
Since diffusion moves materials from an area of higher concentration to the lower, it is described as moving solutes “down the concentration gradient”. The end result is an equal concentration, or equilibrium, of molecules on both sides of the membrane. At equilibrium, movement of molecules does not stop.
Q. What is the movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration?
Diffusion is the movement of particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration?
- Q. When molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration it is moving <UNK> their concentration gradient?
- Q. What is the movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration and does not require energy?
- Q. What is the net movement of molecules from high to low concentrations?
- Q. When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same?
- Q. Is the movement of water along the concentration gradient?
- Q. What is the advantage of using osmotic pressure?
- Q. What is an example of osmotic pressure?
- Q. What is the importance of osmotic pressure?
- Q. What factors does osmotic pressure depend on?
- Q. What causes osmotic pressure to develop in a cell?
- Q. Where is osmosis used in the body?
- Q. What movement is osmosis?
Q. When molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration it is moving <UNK> their concentration gradient?
Osmosis
Q. What is the movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration and does not require energy?
Passive transport does not require energy input. An example of passive transport is diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Carrier proteins and channel proteins are involved in facilitated diffusion.
Q. What is the net movement of molecules from high to low concentrations?
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from an area where they are at a higher concentration to areas where they are at a lower concentration. This is due to the random movement of the molecules. The difference in the concentration of a substance between two areas is called the concentration gradient .
Q. When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same?
During diffusion, when the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the molecules will continue to move across the membrane in both directions.
Q. Is the movement of water along the concentration gradient?
Osmosis refers to the movement of water along a concentration gradient.
Q. What is the advantage of using osmotic pressure?
The osmotic pressure method has the advantage over other method as pressure measurement is around the room temperature and molarity of the solution is used instead of molality. As compare to other colligative properties, its magnitude is large even for every dilute solution.
Q. What is an example of osmotic pressure?
An excellent example of a semipermeable membrane is that inside the shell of an egg. After shell removal is accomplished with acetic acid, the membrane around the egg can be used to demonstrate osmosis. Karo syrup is essentially pure sugar, with very little water in it, so its osmotic pressure is very low.
Q. What is the importance of osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is of vital importance in biology as the cell’s membrane is selective toward many of the solutes found in living organisms. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water actually flows out of the cell into the surrounding solution thereby causing the cells to shrink and lose its turgidity.
Q. What factors does osmotic pressure depend on?
The factors affecting the osmotic pressure are – Solute concentration and temperature.
- Solute concentration is the number of solute particles in a unit volume of the solution that directly determines its potential osmotic pressure.
- Osmotic pressure increases with the increase in temperature.
Q. What causes osmotic pressure to develop in a cell?
What causes osmotic pressure to develop in a cell? Osmotic pressure arises from the tendency of a pure solvent to move through a semipermeable membrane and into a solution containing a solute to which the membrane is impermeable.
Q. Where is osmosis used in the body?
Where Does It Happen? Osmosis occurs in both the small and large intestines, with the majority of osmosis occurring in the large intestine. As your body processes food, it moves from the esophagus to the stomach and then to the small intestine. While there, your body absorbs important nutrients via osmosis.
Q. What movement is osmosis?
Osmosis is the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane driven by a difference in solute concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. A selectively permiable membrane is one that allows unrestricted passage of water, but not solute molecules or ions.