Based on computational analysis and virtual testing, the following observations are made. The hardness (H) of a material tends to increase with an increase in the elastic modulus (E), yield strength (σy) and the strain-hardening exponent (n).
Q. How much elastic potential energy is in a compressed spring?
The work done to stretch or compress the spring is stored in the spring as elastic potential energy. The elastic potential energy of a spring is one half the product of its spring constant multiplied by the square of its deformation.
Table of Contents
- Q. How much elastic potential energy is in a compressed spring?
- Q. Is elastic potential energy affected by mass?
- Q. What is G in material properties?
- Q. Is hardness a material property?
- Q. Are stiffness and hardness related?
- Q. What is difference between stiffness and rigidity?
- Q. What is stiffness of steel?
- Q. Is concrete stiffer than steel?
- Q. What is stiffness in a material?
- Q. How is Young’s modulus related to stiffness?
- Q. What is stiffness of beam?
Q. Is elastic potential energy affected by mass?
Things with kinetic energy can do work. Kinetic energy depends on an object’s mass and velocity. It includes gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Gravitational potential energy depends on an object’s weight and height above the ground.
Q. What is G in material properties?
In materials science, shear modulus or modulus of rigidity, denoted by G, or sometimes S or μ, is a measure of the elastic shear stiffness of a material and is defined as the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain: where = shear stress is the force which acts is the area on which the force acts = shear strain.
Q. Is hardness a material property?
Hardness is the property of a material that enables it to resist plastic deformation, penetration, indentation, and scratching. Therefore, hardness is important from an engineering standpoint because resistance to wear by either friction or erosion by steam, oil, and water generally increases with hardness.
Q. Are stiffness and hardness related?
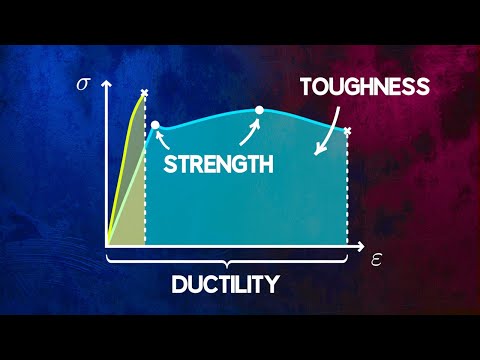
It’s the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs. Stiffness is how a component resists elastic deformation when a load is applied. Hardness is resistance to localized surface deformation.
Q. What is difference between stiffness and rigidity?
Rigidity, also called stiffness, is a measure of elasticity, and represents a material’s resistance to permanent deformation. Rigidity is a material’s resistance to bending, whereas strength is a material’s resistance to breakage. Rigidity is measured by finding the Young’s modulus of a particular material.
Q. What is stiffness of steel?
Stiffness: Stiffness relates to how a component bends under load while still returning to its original shape once the load is removed. A material can have high strength and low stiffness. If a metal cracks easily, it has low strength, but if it has low stiffness, it can deflect a high load.
Q. Is concrete stiffer than steel?
The most asked question was is steel stronger than concrete? The short answer is No. The compressive strength of concrete is more than the steel, to handle tension forces steel bars are used in the concrete because of the weakness of concrete. The wall made of concrete alone is much stronger than the mass of steel.
Q. What is stiffness in a material?
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force. The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Q. How is Young’s modulus related to stiffness?
Stiffness is resistance to elastic deformation. Young’s modulus Y=stress/strain. so, for given stress if young’s modulus is high then elastic deformation is small. So, stiffness and young’s modulus are proportional to each other.
Q. What is stiffness of beam?
In structural engineering, beam stiffness is a beam’s ability to resist deflection, or bending, when a bending moment is applied. Beam stiffness is affected by both the material of the beam and the shape of the beam’s cross section. Beam stiffness is an important factor in bridge design.