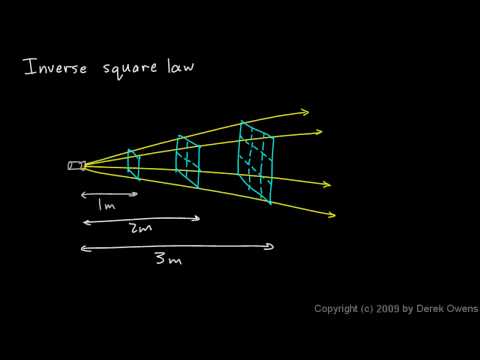
Inverse Square Law, General Any point source which spreads its influence equally in all directions without a limit to its range will obey the inverse square law. Point sources of gravitational force, electric field, light, sound or radiation obey the inverse square law.
Q. Which of the following forces does not obey inverse square law?
Reason : Nuclear force do not obey inverse square law.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which of the following forces does not obey inverse square law?
- Q. Does strong nuclear force obeys inverse square law?
- Q. Is nuclear force inverse square law?
- Q. What is the range of the strong nuclear force?
- Q. Do all forces follow the inverse square law?
- Q. What is the inverse square law in photography?
- Q. How do you do inverse law?
- Q. How does the inverse square law relate to light?
Q. Does strong nuclear force obeys inverse square law?
No, neither the strong nuclear force nor the weak nuclear force follow the inverse square law. The weak nuclear force is a Yukawa-type force. Such a force is characterized by a potential in the form . The strong nuclear force does not decrease with distance.
Q. Is nuclear force inverse square law?
These particles provide both attractive and repulsive short-range forces that overcome the long-range repulsive electrical force and hold nucleons together at close range. The Strong Nuclear Force concept requires believing that forces exist in three-dimensional space whose strengths don’t follow an inverse square law.
Q. What is the range of the strong nuclear force?
The nuclear force is powerfully attractive between nucleons at distances of about 1 femtometre (fm, or 1.0 × 10−15 metres), but it rapidly decreases to insignificance at distances beyond about 2.5 fm. At distances less than 0.7 fm, the nuclear force becomes repulsive.
Q. Do all forces follow the inverse square law?
1 Answer. No, it’s the forces mediated by point particles with no mass and charge that follow the the 1/r^2 rule. The strong force’s gluons are massless, so at first glance they could follow the inverse square. However, they also have color charge (as well as electric), which has entirely different physics.
Q. What is the inverse square law in photography?
In all of its overly technical glory, the Inverse Square Law– as it applies to photography– is an equation that relates the intensity of a light source to the illumination it produces at any given distance. It means that doubling the flash-to-subject distance reduces the light falling on the subject to one-quarter.
Q. How do you do inverse law?
All you need to do is take the distance from the light to the subject and then inverse the square of it. So, if the distance is one foot, the inverse of one squared comes down to one. In other words, the light you get is 100 percent—no adjustment is necessary.
Q. How does the inverse square law relate to light?
The inverse-square law works as follows: If you double the distance between subject and light source, it illuminates a surface area four times greater than the one before. …