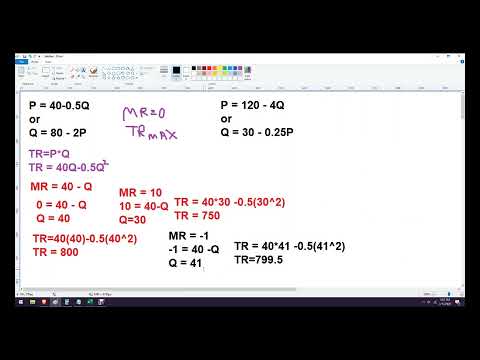
Total revenue is maximized at the price where demand has unit elasticity.
Q. What happens to revenue when demand is elastic?
If demand is elastic at a given price level, then should a company cut its price, the percentage drop in price will result in an even larger percentage increase in the quantity sold—thus raising total revenue.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens to revenue when demand is elastic?
- Q. What happens to the total expenditures for a product with elastic demand when its price goes up?
- Q. How do firms increase revenue?
- Q. What is total revenue equal to?
- Q. What is the formula of Mr?
- Q. What is the relationship between price and total revenue?
- Q. Is MC equal to VC?
- Q. How is VC calculated?
- Q. What is MC in microeconomics?
- Q. How do you find TC from MC?
- Q. How is total cost calculated?
- Q. What is marginal cost and average cost?
- Q. What is the relationship between AC and MC?
- Q. Why does MC cut AC at its minimum?
- Q. Where does MC cut AC below?
- Q. What can we say about MC when AC is minimum Mcq?
- Q. What is AVC at its minimum?
- Q. What is the difference between TC and TVC called?
- Q. Can TVC and TC curves meet?
- Q. Which cost is zero when output is zero?
- Q. How is TFC calculated from TC?
Q. What happens to the total expenditures for a product with elastic demand when its price goes up?
Total expenditures decrease because people buy less of the product when the price increases.
Q. How do firms increase revenue?
At low quantities and high prices, a firm can increase its revenues by moving down the demand curve—to lower prices and higher output. Marginal revenue is positive….Marginal Revenue and the Elasticity of Demand
- Marginal revenue is always less than the price.
- Marginal revenue can be negative.
Q. What is total revenue equal to?
Total revenue is the full amount of total sales of goods and services. It is calculated by multiplying the total amount of goods and services sold by their prices. Marginal revenue is the increase in revenue from selling one additional unit of a good or service.
Q. What is the formula of Mr?
A company calculates marginal revenue by dividing the change in total revenue by the change in total output quantity. Therefore, the sale price of a single additional item sold equals marginal revenue. For example, a company sells its first 100 items for a total of $1,000.
Q. What is the relationship between price and total revenue?
Price and total revenue have a negative relationship when demand is elastic (price elasticity > 1), which means that increases in price will lead to decreases in total revenue. Price changes will not affect total revenue when the demand is unit elastic (price elasticity = 1).
Q. Is MC equal to VC?
Yes, Variable Cost (VC) of producing units of output is the value of the integral of Marginal Cost (MC) over the range .
Q. How is VC calculated?
To determine the total variable cost the company will spend to produce 100 units of product, the following formula is used: Total output quantity x variable cost of each output unit = total variable cost.
Q. What is MC in microeconomics?
In economics, the marginal cost of production is the change in total production cost that comes from making or producing one additional unit.
Q. How do you find TC from MC?
The Average Cost (AC) for q items is the total cost divided by q, or TC/q. You can also talk about the average fixed cost, FC/q, or the average variable cost, TVC/q. The Marginal Cost (MC) at q items is the cost of producing the next item. Really, it’s MC(q) = TC(q + 1) – TC(q).
Q. How is total cost calculated?
The formula for calculating average total cost is:
- (Total fixed costs + total variable costs) / number of units produced = average total cost.
- (Total fixed costs + total variable costs)
- New cost – old cost = change in cost.
- New quantity – old quantity = change in quantity.
Q. What is marginal cost and average cost?
Marginal cost is the change in total cost when another unit is produced; average cost is the total cost divided by the number of goods produced.
Q. What is the relationship between AC and MC?
There exists a close relationship between AC and MC. i. Both AC and MC are derived from total cost (TC). AC refers to TC per unit of output and MC refers to addition to TC when one more unit of output is produced.
Q. Why does MC cut AC at its minimum?
When the MC is smaller the AC, the AC decreases. This is because when the extra unit of output is cheaper than the average cost then the AC is pulled down. Similarly, when the MC is greater than the AC, the AC is pulled up. The point of intersection between the MC and AC curves is also the minimum of the AC curve.
Q. Where does MC cut AC below?
The fall is due to the economies of scale. But beyond a point (M), i.e., when output is expanded too much, both AC and MC start rising and now MC is above AC, i.e., the marginal cost is greater than the average cost. That is why MC cuts AC from below at its lowest point.
Q. What can we say about MC when AC is minimum Mcq?
AC will reach a minimum at a level of output that is less than that at which MC reaches a minimum. both AC and MC will reach a minimum at the same level of output. If a firm’s marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, then the firm should. a.
Q. What is AVC at its minimum?
AVC attains a minimum at an output of 12. The minimum of AVC always occurs where AVC = MC.
Q. What is the difference between TC and TVC called?
Since the TFC curve is horizontal, the difference between the TC and TVC curve is the same at each level of output and equals TFC. The TFC curve is parallel to the horizontal axis while the TVC curve is inverted-S shaped.
Q. Can TVC and TC curves meet?
Explain. No. They don’t intersect each other because they are parallel to each other.
Q. Which cost is zero when output is zero?
In the short run, total cost is equal to zero when output is equal to zero. In the long run, total cost is equal to zero when output is equal to zero.
Q. How is TFC calculated from TC?
Fixed Cost Formula Isolate all of these fixed costs to the business. Add up each of these costs for a total fixed cost (TFC). Identify the number of product units created in one month. Divide your TFC by the number of units created per month for an average fixed cost (AFC).